FLOPS is a popular measure of computer hardware performance. BOINC projects reward credits based on FLOPS. Users complain that that credits rewarded by BOINC projects are very inconsistent between projects. One of the reasons is that FLOPS concept is not well defined, it’s fuzzy.
What is FLOPS?
FLoating point Operations Per Second (FLOPS) from the definition is a number of floating point operations computer can perform within one second.
Peak FLOPS equals to Number of Cores∗Average frequency∗Operations per cycle
So far so good.
Floating point stands for the type of the number; real numbers are usually represented in the programming languages as a variable of the type float (FP32 – single precision, occupies 32 bits in computer memory) or type double ((FP64 – double precision, occupies 64 bits in computer memory)
Operations stand for operations like addition and multiplication; the problems arising here are:
- different architectures have different types of instructions sets; for example some new processors can perform addition and multiplication within just one instruction but usually it’s counted as two FLOPS; sine function can take several more instructions on one machine than on another;
- on some processors (GPUs) integer and floating point operations share some resources – thus if also integer numbers are calculated, peak FLOPS is unachievable;
Theoretical peak FLOPS can be calculated using above equation, or more realistic measure taken by running one of the benchmark codes, like Whetstone or LINPACK. As FLOPS performance measures have several shortcomings, new benchmarks are proposed, like HPCG.
As you see, comparing FLOPS for different machines without knowing WHAT KIND OF FLOPS they are can become comparing apples and plums.
BOINC project rewards 200 credits (Cobblestone) for one day of CPU time on a reference computer that does 1 GigaFLOPS based on the Whetstone benchmark. Therefore computing power can be calculated as GigaFLOPSs = RAC/200.
A snippet of Whetstone benchmark code:

BOINC formula RAC and GFLOPS
For calculations and comparison I have used base NVIDIA GTX 1060 6GB GFLOPS (no boost, no overclocking).
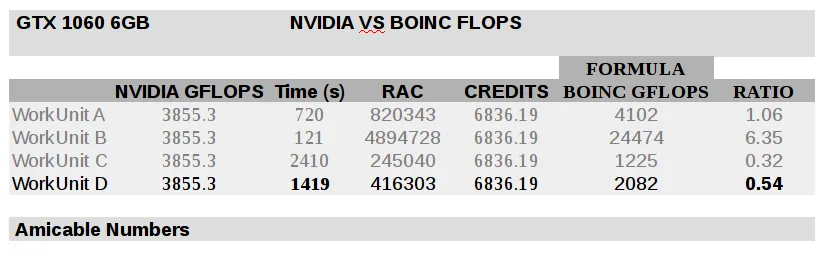
Amicable Numbers
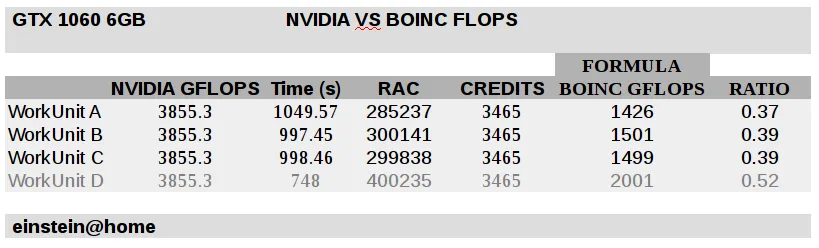
The time to complete a WU varies, although most workunits are quite consistent and take around 1500 seconds. For GTX 1060 6GB maximum RAC is ~ 400 000, while performed GFLOPS calculated with BOINC formula is ~2000, which is around ~50% of the nominal peak value.
einstein@home
The time to complete a WU is recently more consistent than in previous case, most units take around 1000 seconds. For GTX 1060 6GB maximum RAC is ~ 300 000, while performed GFLOPS calculated with BOINC formula is ~1500, which is just under ~40% of the nominal peak value.