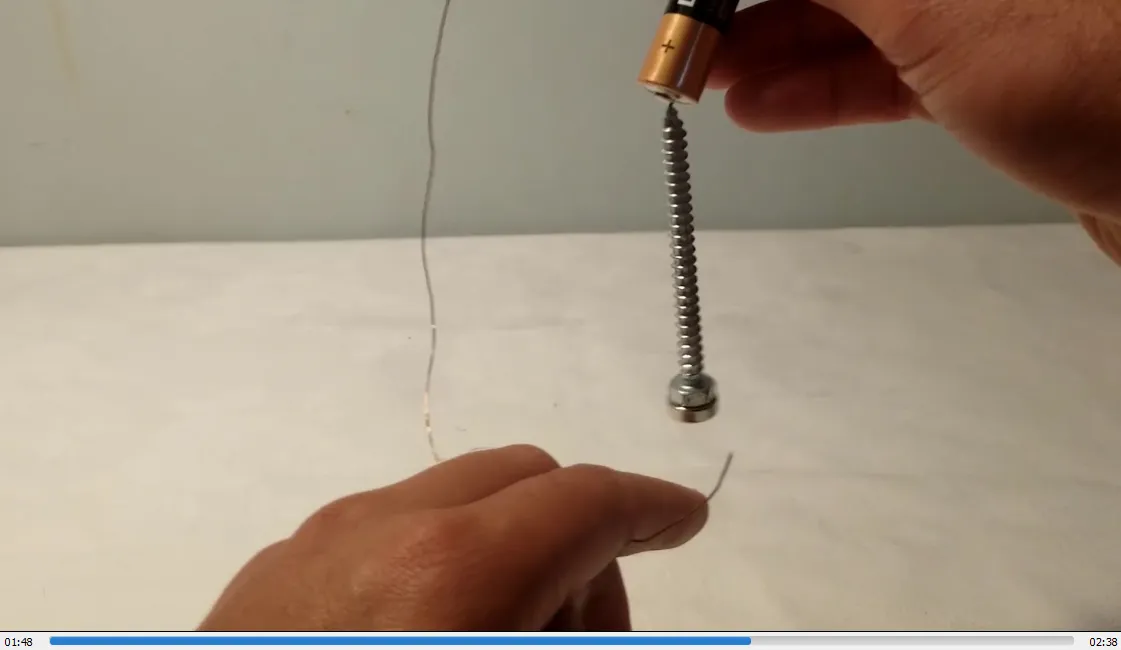
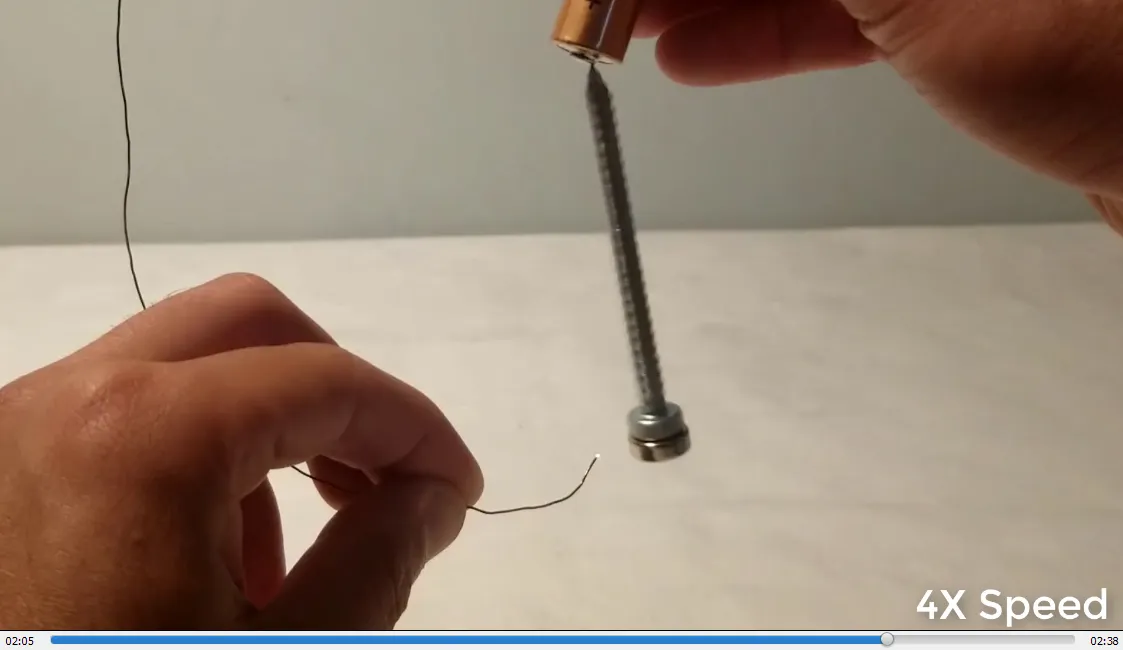
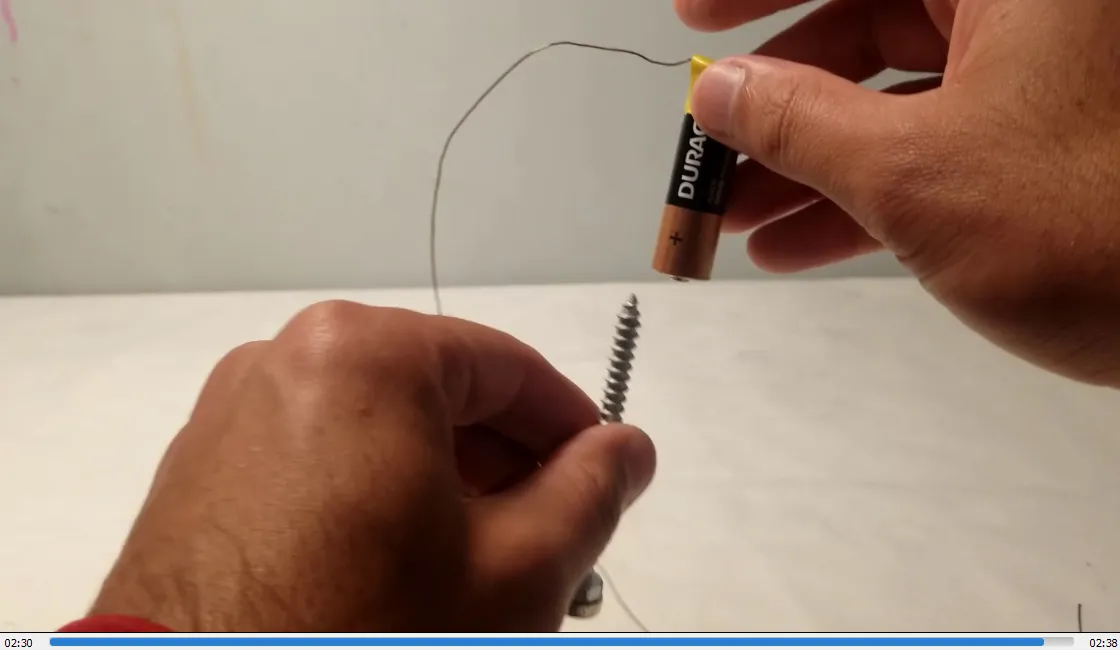
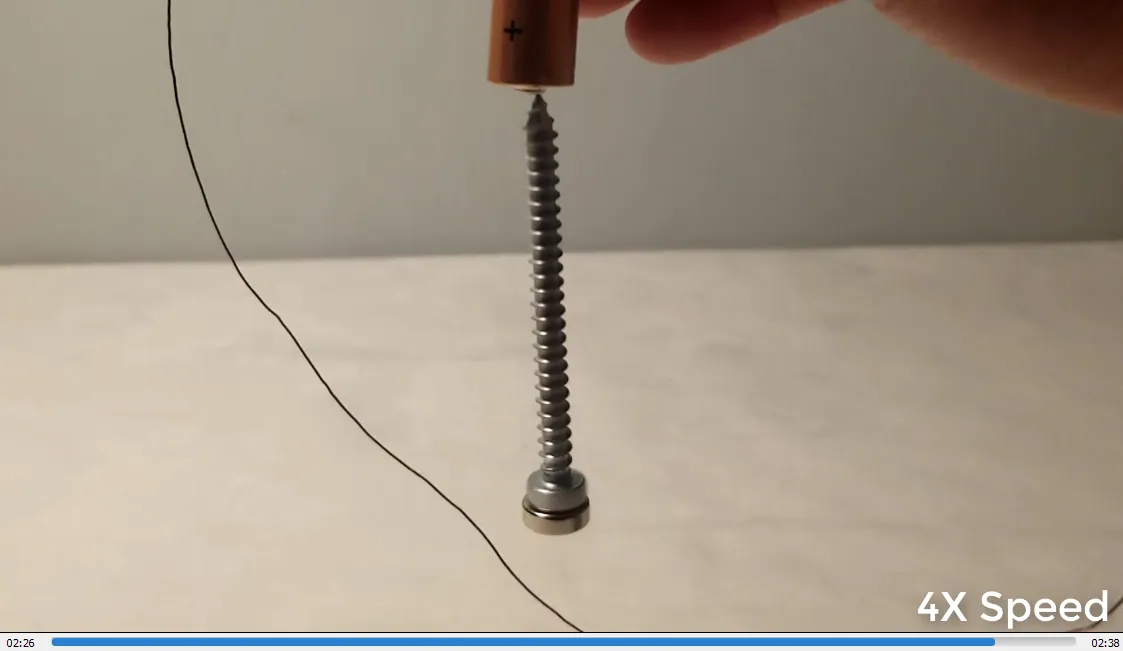
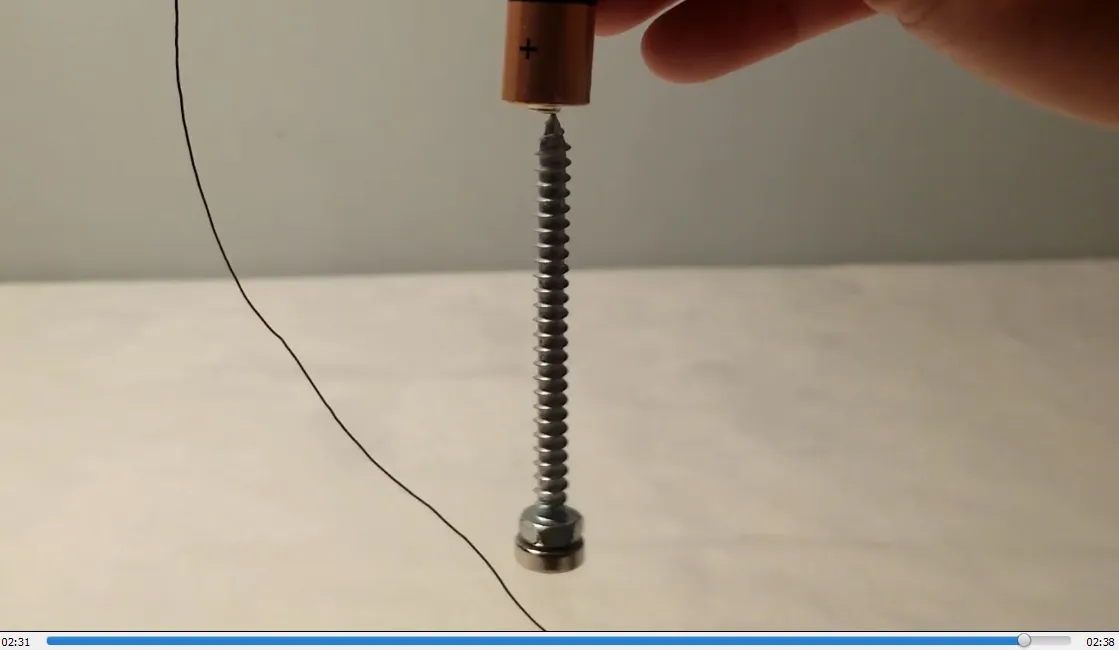
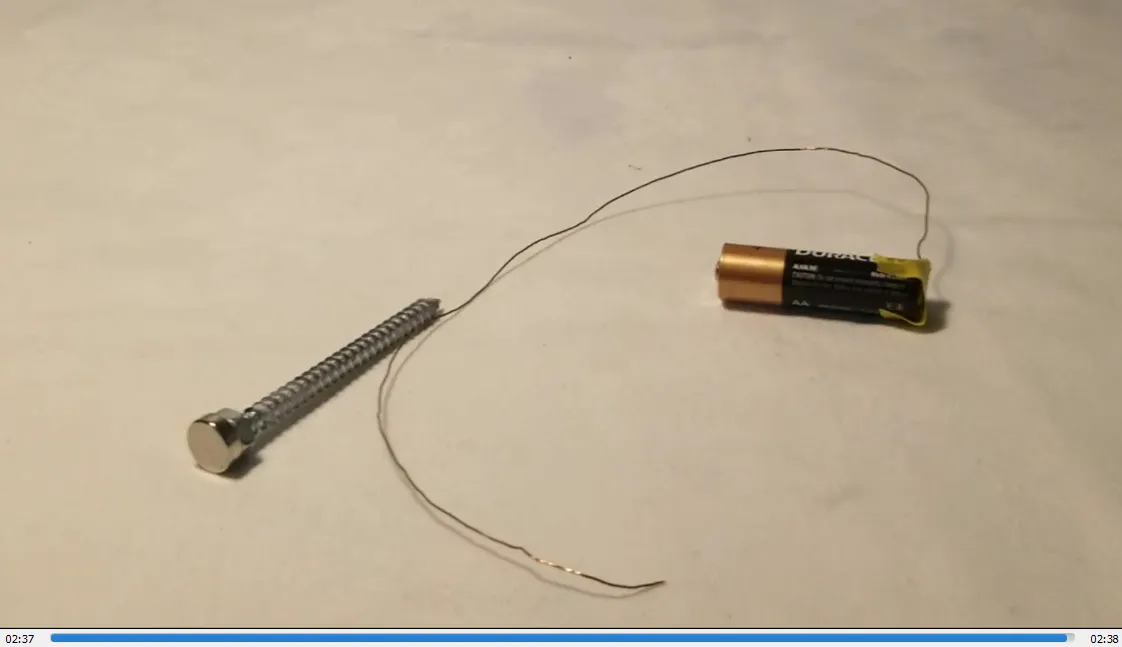
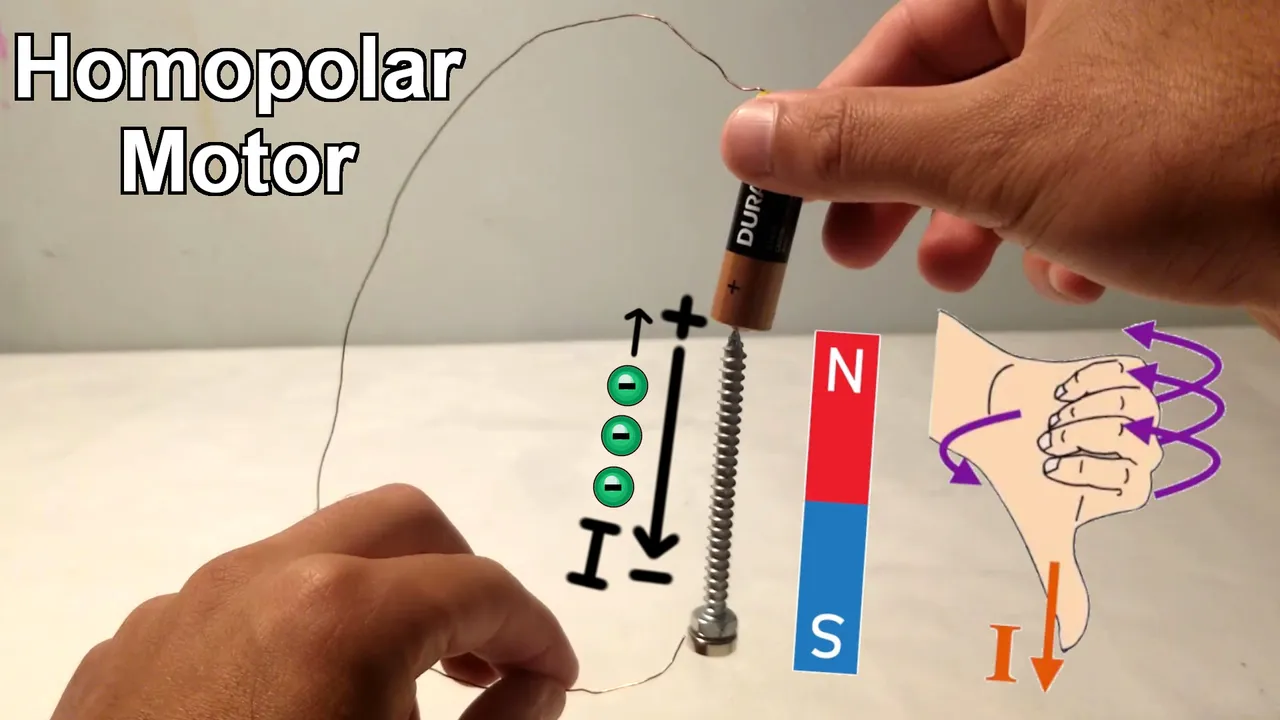
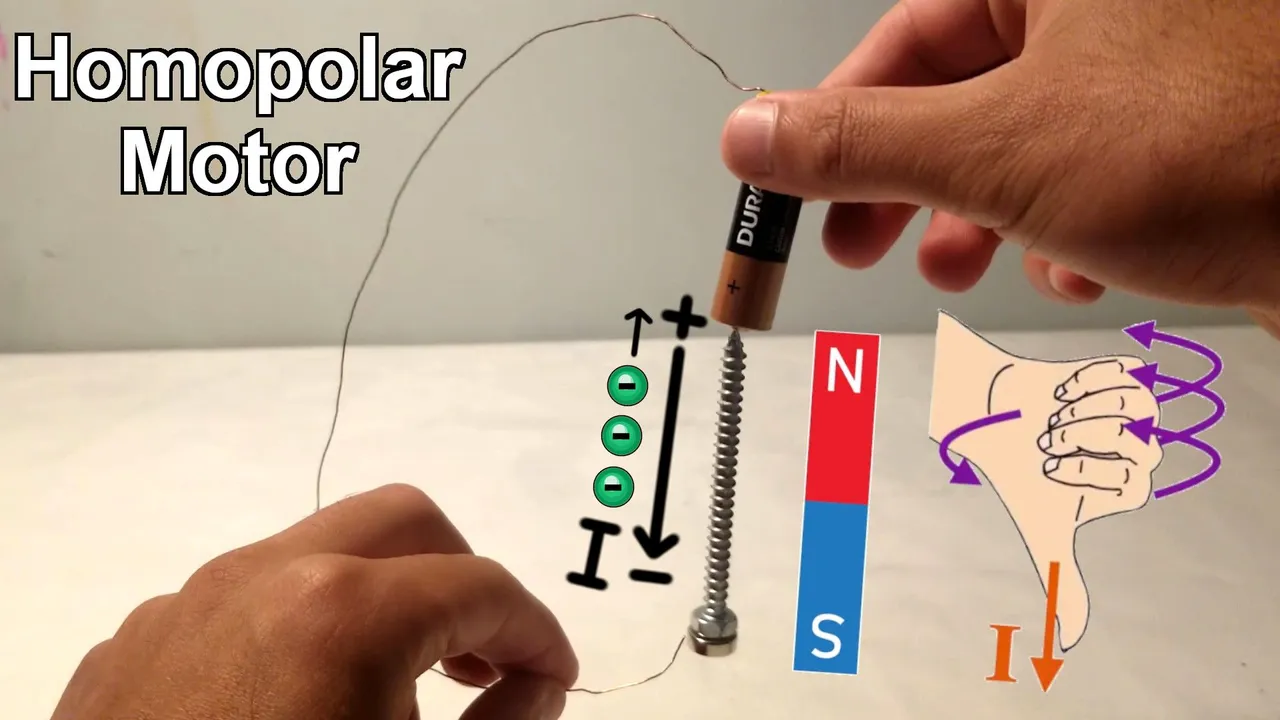
In #MESExperiments 41 I demonstrate a simple homopolar motor using just some tape, a 1.5-volt battery, a copper wire, a steel screw, and a magnet. When the magnet is attached to the screw, it magnetizes the screw, allowing it to stick to the battery. Closing the circuit by making contact between the magnet or the bottom of the screw and the battery causes the screw to rotate rapidly. This experiment effectively demonstrates how a basic electromagnetic circuit can generate rapid physical rotation, functioning as a simple motor.
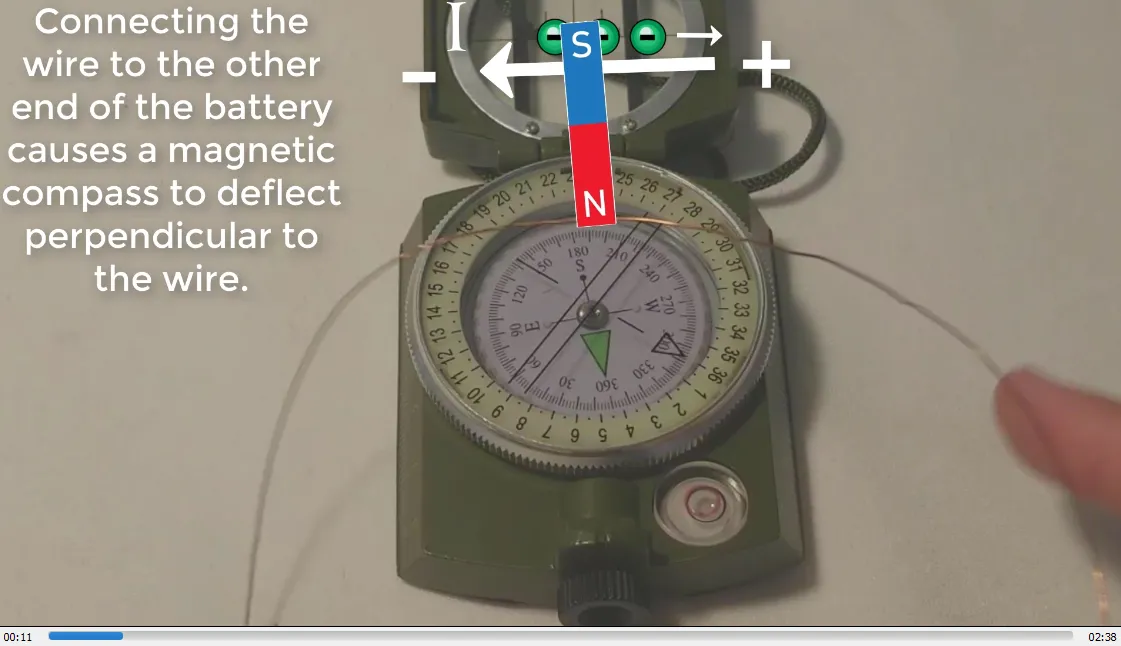
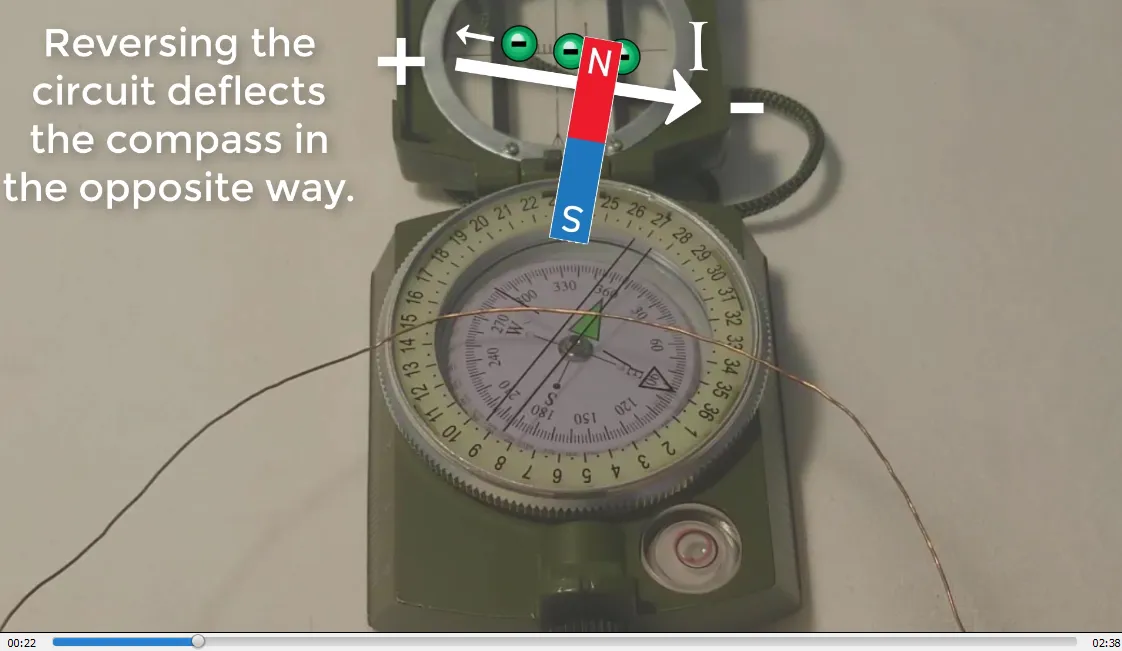
I also illustrate how a magnetic compass behaves near a magnet and a wire in an electric circuit. The compass needle deflects away from the magnet's North Pole and towards the South Pole of the magnet. Note that a compass determines geographic North, which is actually Earth's magnetic South Pole. In an electric circuit, the compass needle deflects perpendicular to the wire.
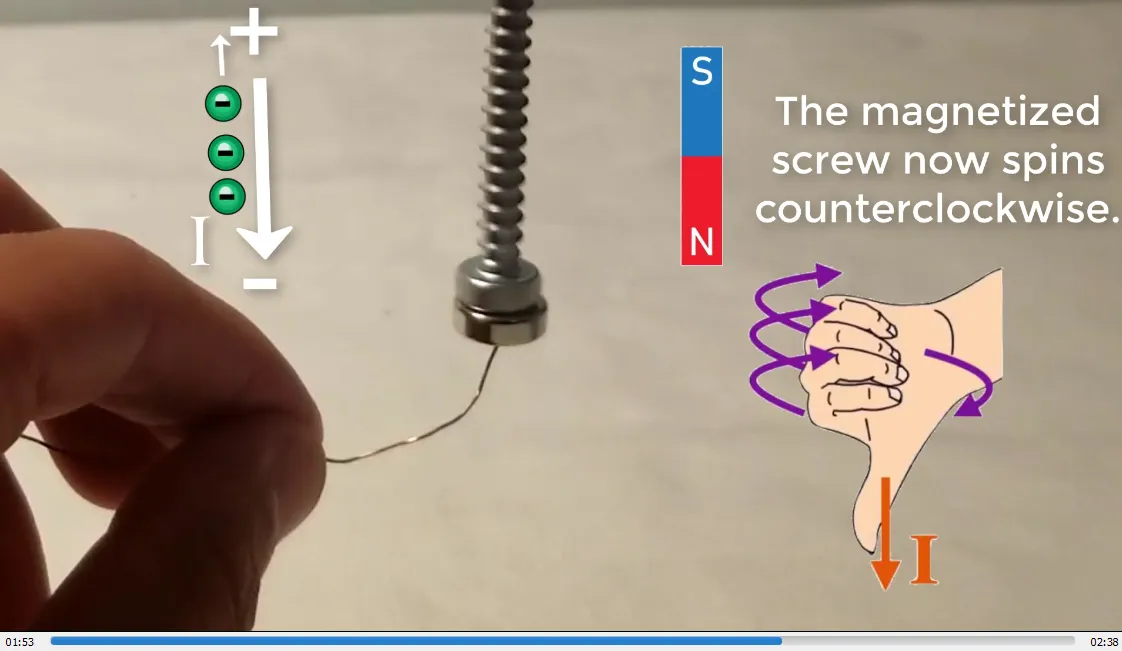
Additionally, I include information on the direction of current, the direction of electron flow (opposite to current), and the polarity of the magnetized screw. The corresponding spin directions are as follows:
Clockwise spin: North Pole upwards, current flowing downwards, electron flow upwards.
Counterclockwise spin: North Pole downwards, current flowing downwards, electron flow upwards.
Links to more info and mainstream explanations
- Homopolar motor wiki: https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Homopolar_motor
- Mainstream diagrams and explanation: https://www.sparkfun.com/news/1332
- Various different homopolar motors:

Timestamps
- Taping a copper wire to a battery: 0:00
- Current deflects magnetic compass perpendicular to wire: 0:05
- Reversing circuit deflects compass in opposite direction: 0:13
- Non-magnetized steel screw does not stick to battery: 0:25
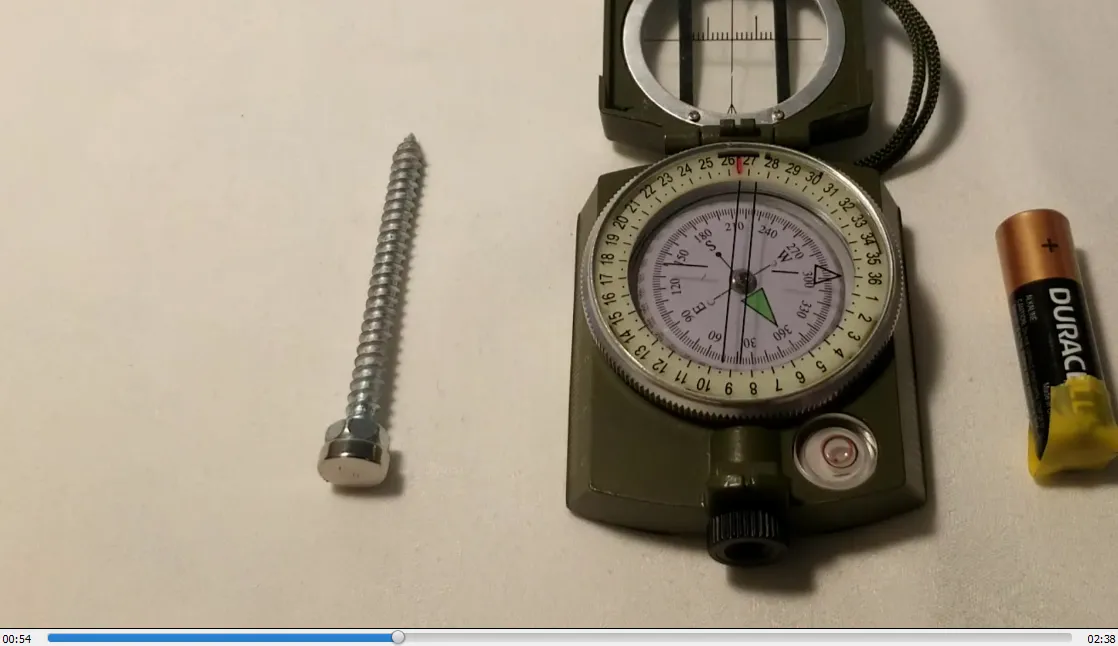
- Compass points to South Pole of magnet and away from the North Pole: 0:33
- Attaching a magnet to the screw magnetizes it: 0:46
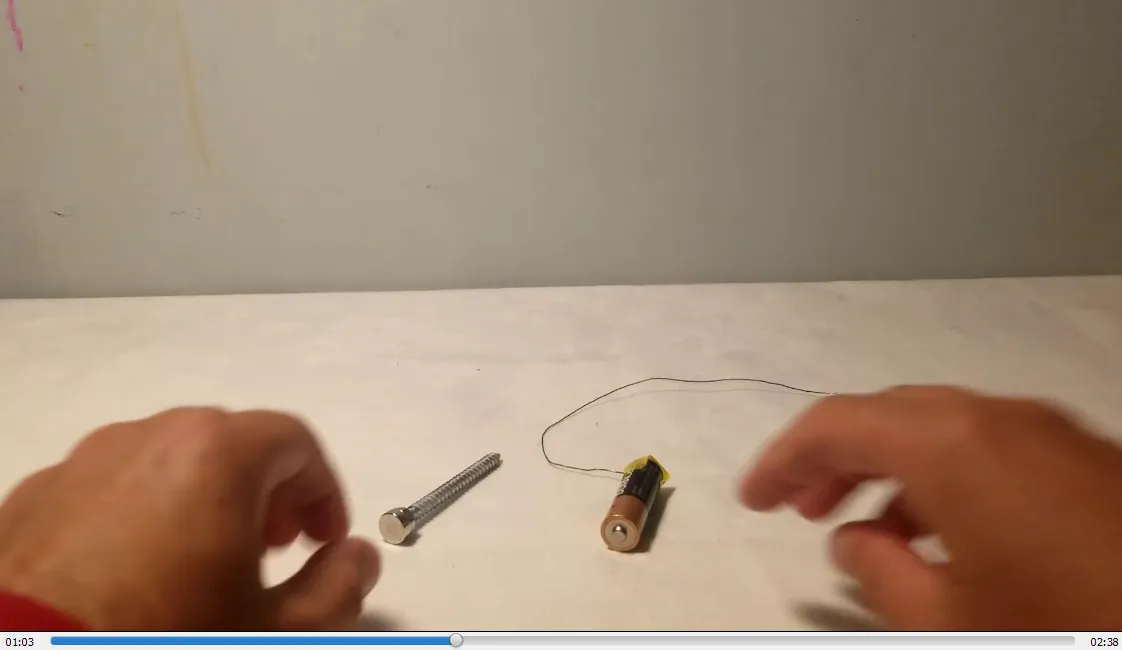
- Magnetized screw sticks to battery: 1:03
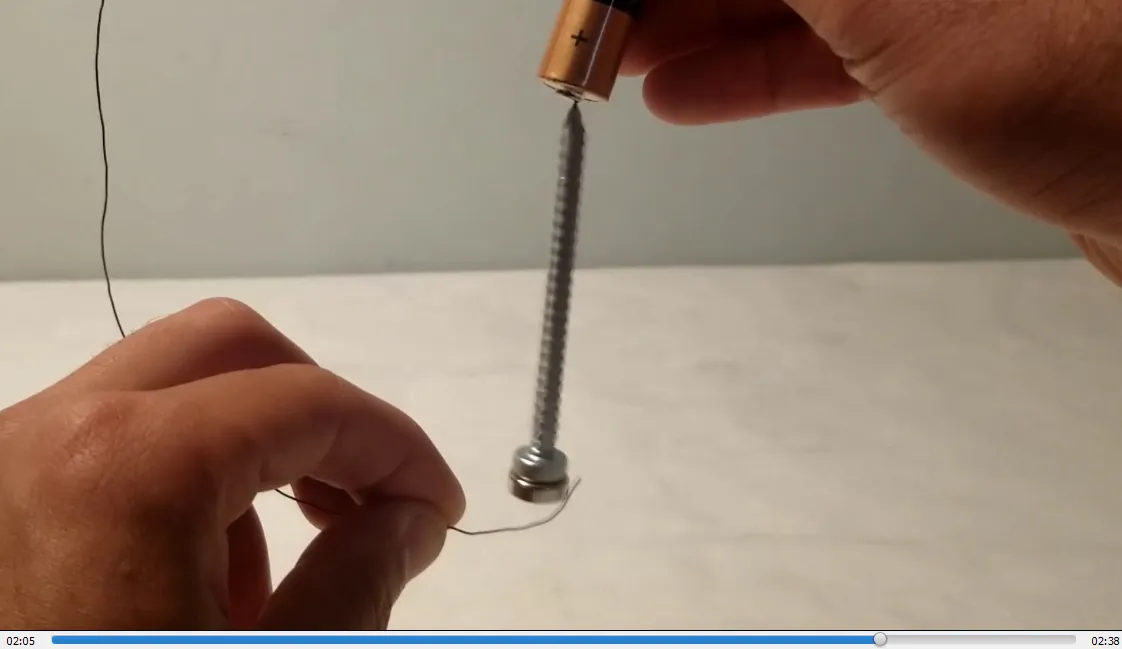
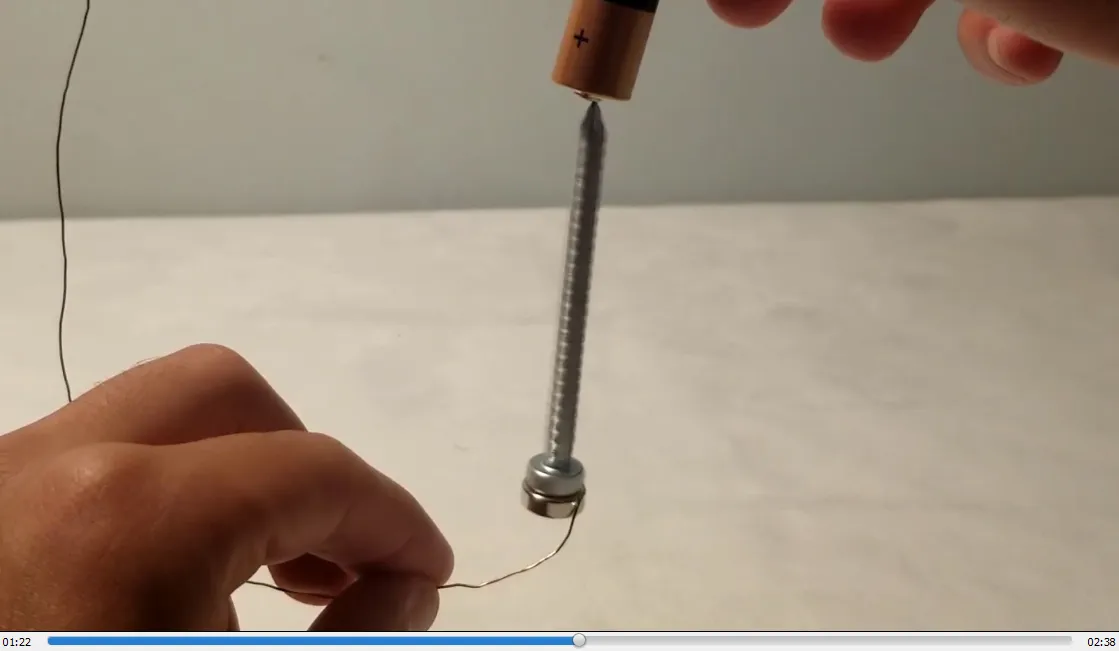
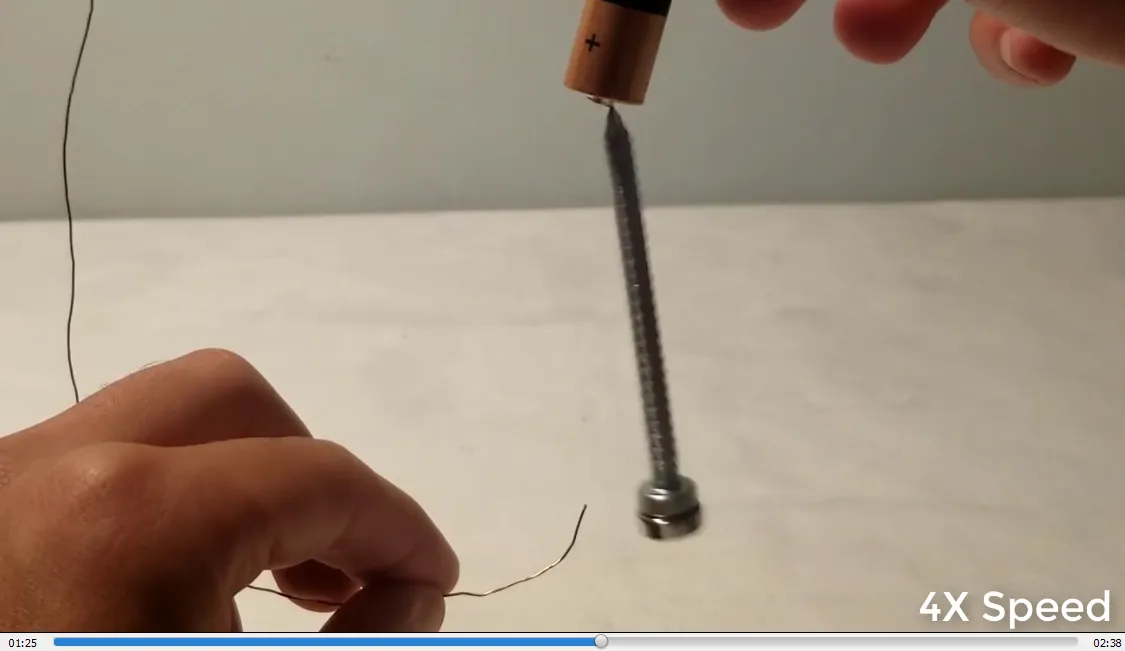
- Contacting the magnetized screw causes it to spin clockwise: 1:12
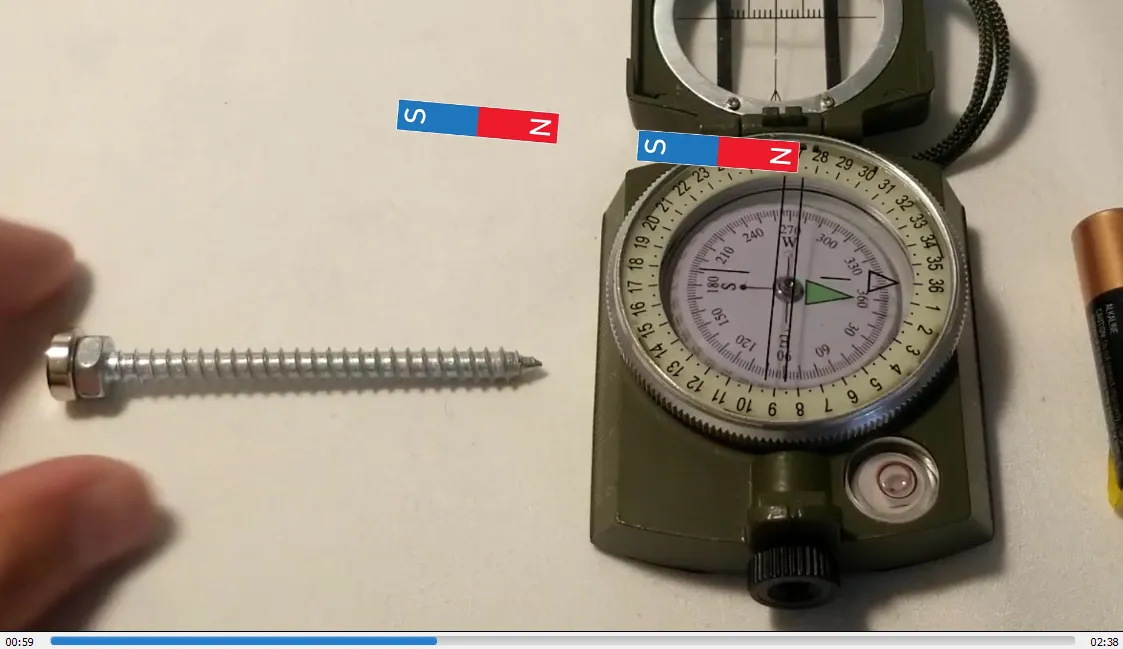
- Turning the magnet the other way causes the screw to spin in opposite direction: 1:38
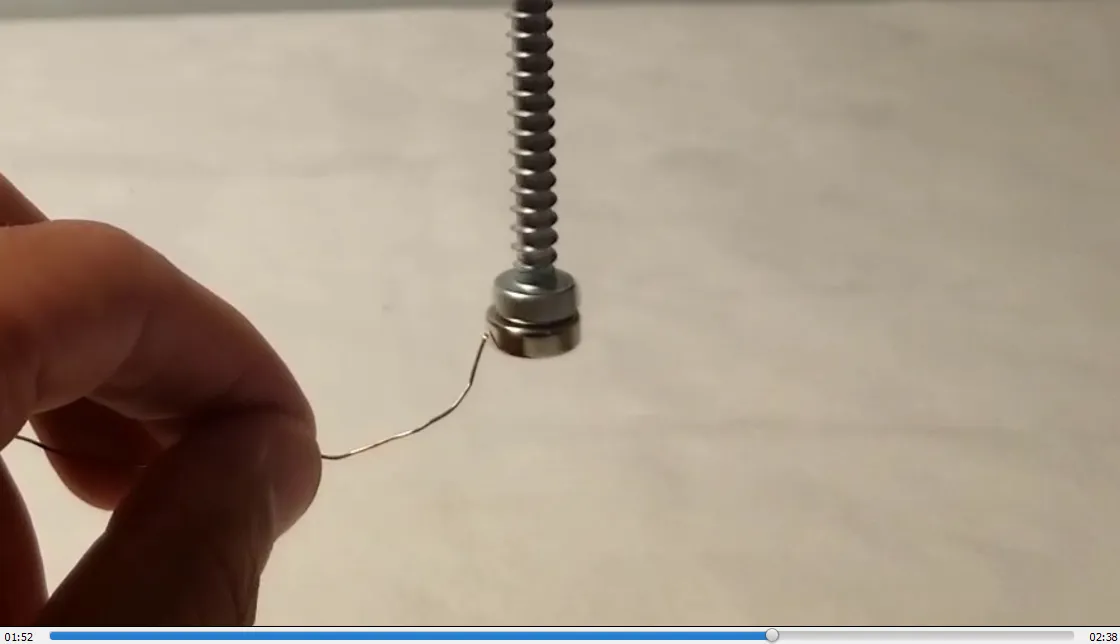
- Magnetized screw now spins counterclockwise: 1:52
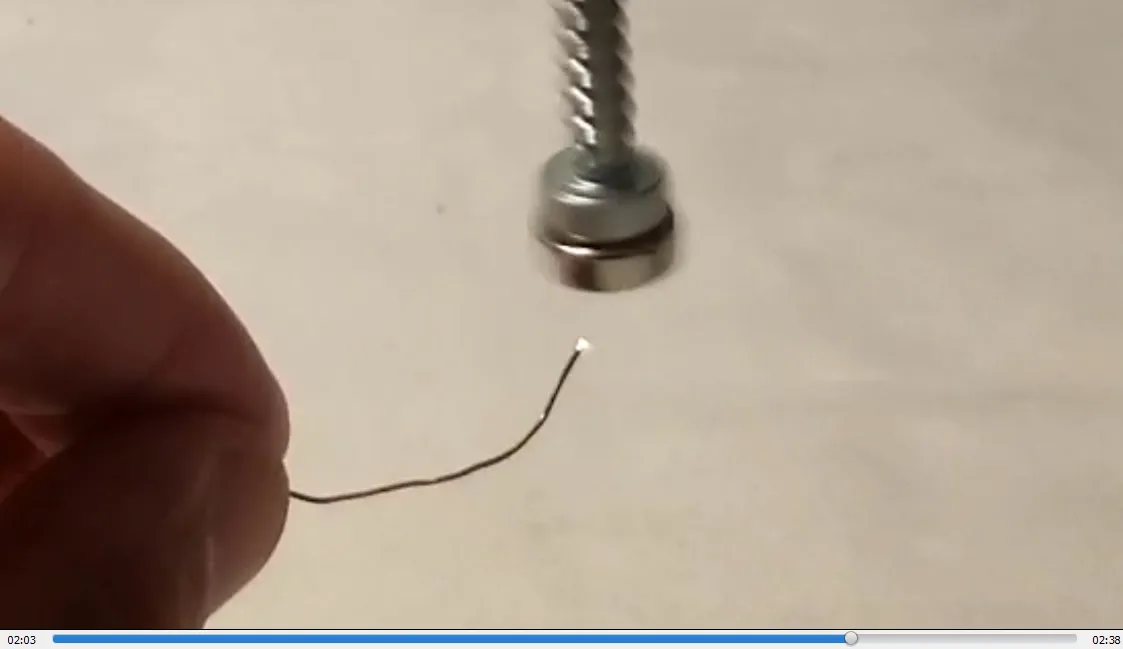
- Sparks visible at the tip of the wire: 1:59
- End of experiment: 2:33
Stay tuned for #MESExperiments 42...
More Experiments
MES Experiments video series - (Hive playlist) - DRAFT Experiments - MES Links
Screenshots of Experiment
For reference here are screenshots of the experiment.
Taping a copper wire to the battery

Current in wire deflects magnetic compass perpendicular to wire


Non-magnetized steel screw does not stick to battery



Compass needle points to South pole of magnet and away from the North Pole



Magnet magnetizes steel screw



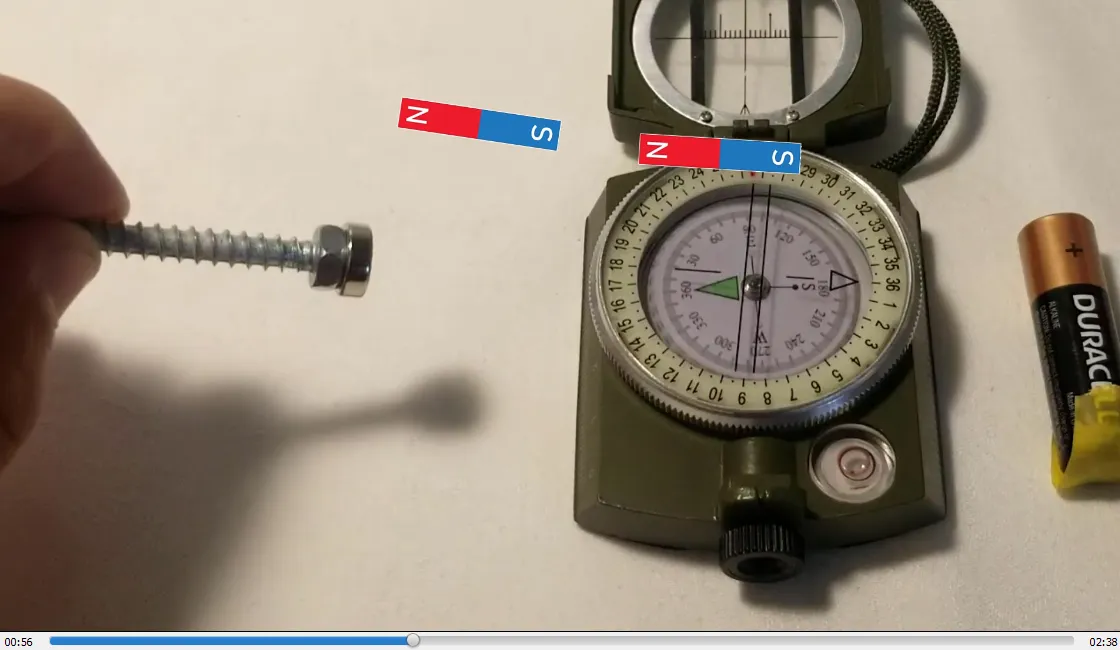
Homopolar screw motor: Spinning clockwise
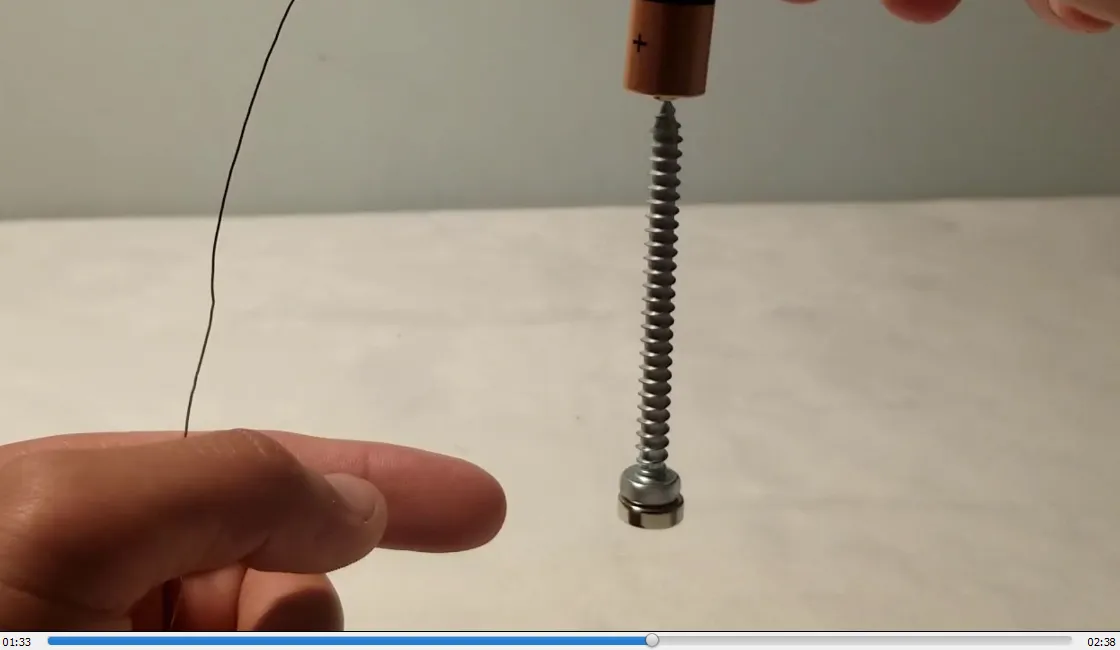







Reversing polarity of magnet reverses spin direction