This post contains a video that investigates the causes of inflation as well as the costs of inflation. There are several causes of inflation. These include cost push inflation, demand pull inflation, currency exchange rate induced inflation and inflation caused by monetary policy.
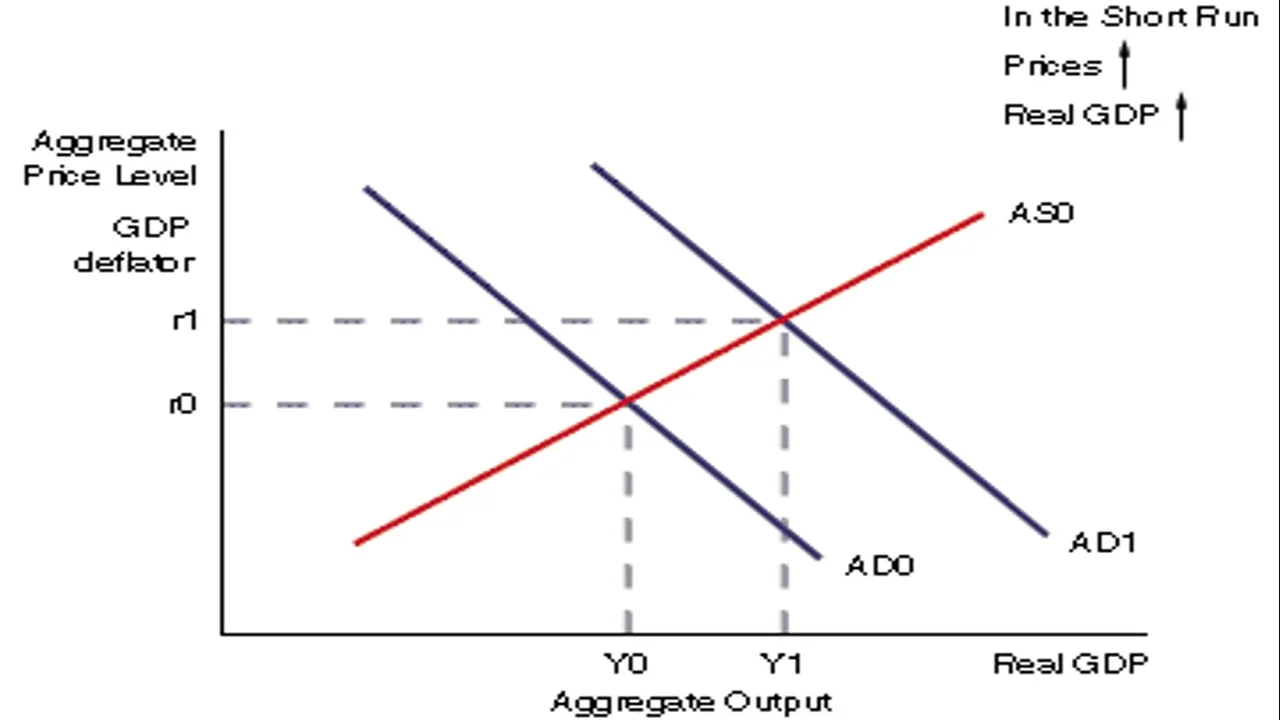
Attention is typically given to demand pull inflation and cost push inflation. Demand pull inflation is caused by increases in aggregate demand that cannot be met immediately with existing supply. This is often related to the full or close to full employment of existing resources. As extra capacity does not exist, prices are forced higher.
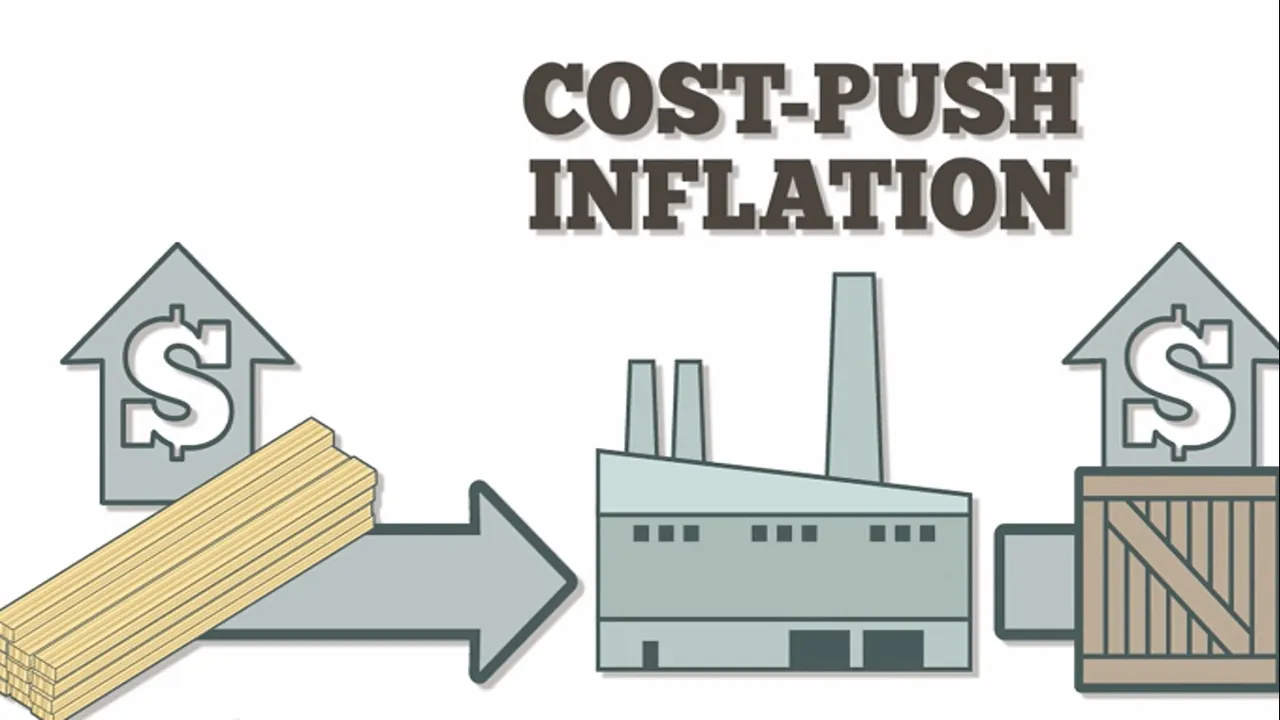
Cost push inflation affects supply rather than demand. Demand may not increase but supply becomes limited or more costly. Increased cost of raw materials, higher wages or capital can push overall costs up. These cost increases are passed on to consumers in the form of higher prices, hence the occurrence of inflation. Shortages can create the same effect of shifting the supply curve to the left and raising prices.
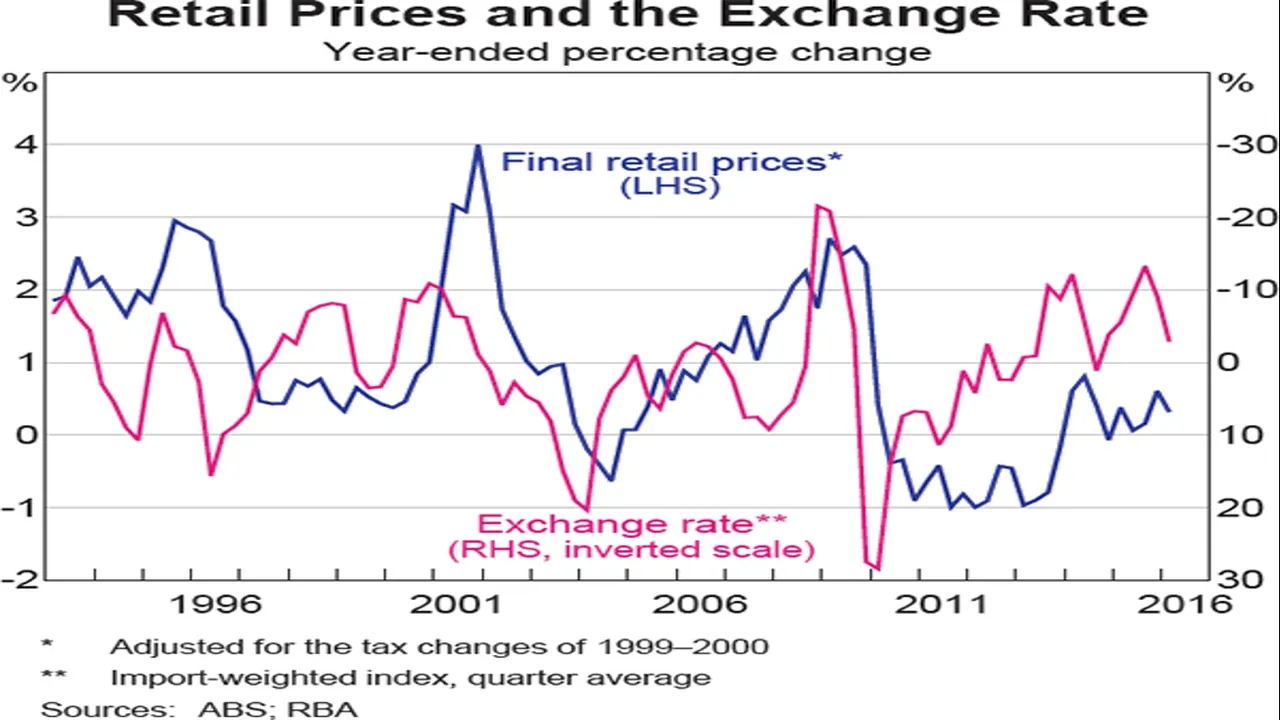
A weaker exchange rate can cause inflation and in some cases hyperinflation. Uncompetitive products produced in the home country can result in higher imports and lower exports, which reduces demand for the country’s currency and, therefore, reduces the value of the currency, hence, making products and services more expensive (more expensive imports and more expensive imported components of goods). Even more concerning than uncompetitive home produced goods is the outflow of capital. For example, the outflow of capital from Zimbabwe in late 90s literally destroyed the value of the Zimbabwean dollar and caused unimaginable hyperinflation. This is often caused by the loss of confidence in the value of the currency; in sort, creating a self-fulling prophesy.
The most concerning cause of inflation in western countries is the manipulation of money supply by central banks. Central banks can produce as much money as they like literally out of thin air. This is what is called fiat money (backed by the promise of value rather than physical assets such as gold). There is a strong relationship between increasing money supply and inflation as the video explains. The typical explanation for increasing money supply is to generate economic growth. Increased money supply lowers interest rates, which reduces the cost of borrowing, hence stimulates investment. Lower interest rates also stimulates more consumption and there is evidence suggesting that the effect on consumption is greater than the effect on investment. Investment is often more sensitive to the availability of good investment opportunities rather than the cost of borrowing capital. John Keynes referred to this stimulation of investment as a response to our ‘animal spirits’.
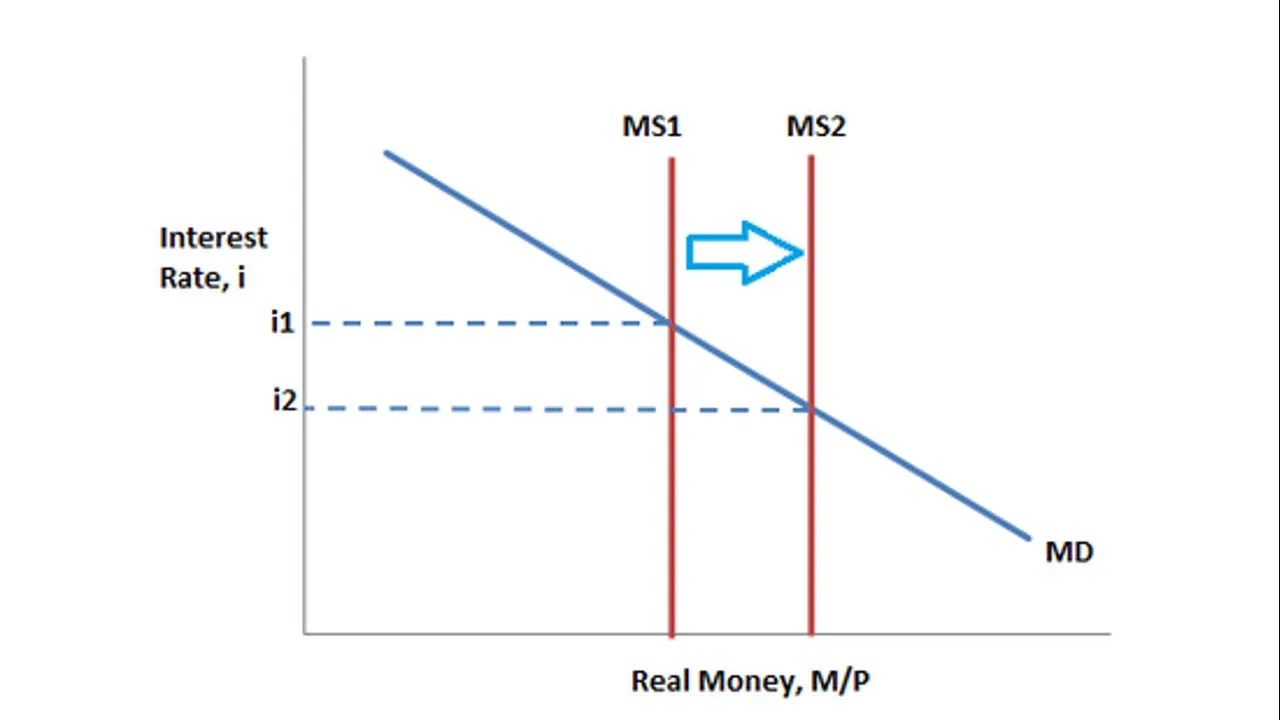
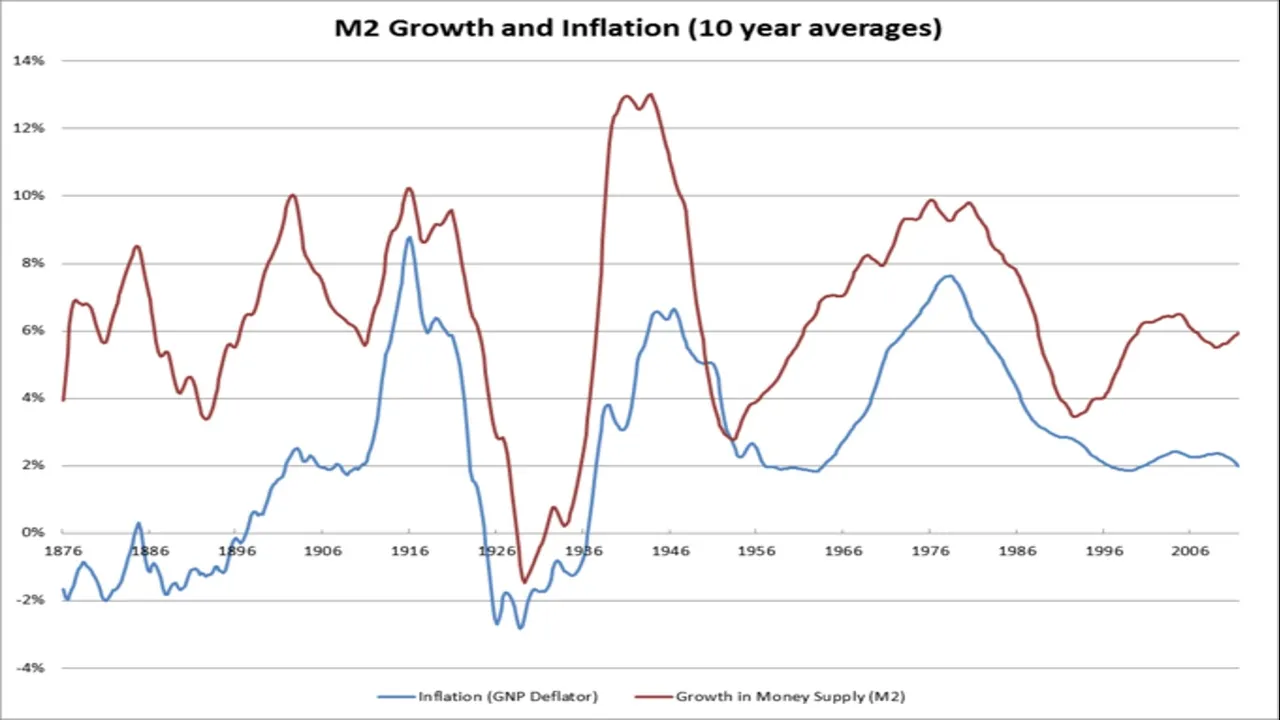
The video also explains the costs of inflation. Textbooks include costs such as shoe leather costs which relates to the costs of activities such as making more trips to the bank (less relevant with electronic banking) and menu costs which relates to the cost of frequent price changes (less costly with electronic pricing). The video places the most emphasis on the cost of erosion of wealth and savings caused by inflation, particularly hyperinflation. Venezuela is an example of a country which has been hit particular hard by hyperinflation and its citizens have seen most of their wealth eroded.
The video can be watched at the link below:
The macroeconomic series can be accessed at:
The official Spectrum Economics website can be accessed at: https://www.spectrumecons.com
For more exciting videos go to my YouTube channel at https://www.youtube.com/channel/UCILwyLtjl7ZTlYOqFkAwLzw
You can find me on LinkedIn at: https://www.linkedin.com/in/waynedavies-spectrumecons/
You can find me on Facebook at: https://www.facebook.com/SpectrumEconomics/
You can find me on Steemit at: @spectrumecons

