Repository
https://github.com/igormuba/EthereumSolidityClasses/tree/master/class5
What Will I Learn?
- Create functions for vanilla data types
- Using and importing libraries
- Libraries and security uses
Requirements
- Internet connection
- Code editor
- Browser
Difficulty
- Intermediate
Tutorial Contents
Let us get started with using libraries. On the previous lesson, available at
@igormuba/part-4-ethereum-solidity-custom-access-modifiers-security-breach-alerts-assert-and-require-pt-4
I have talked about custom access modifiers, which allowed us to customize the access authorization logic beyond what the basic private, public, internal and external allowed us.
Now, for libraries, we can customize the functionality of Solidity data types. The vanilla functions for String types, for example, allow you to splice, concatenate and work in different ways with string. Here let us implement new functions for uint types.
Solidity still has a very limited syntax.
For example, other programming languages have native keywords/functions to change a string to lowercase or uppercase automatically, but Solidity don't! Yes, if you want to lowercase your string you will need to build a library for that!
The library keyword
By using the keyword library we can create what ressembles a contract, the difference is that contracts are inherited by other contracts, libraries are inherited by data types, like uint in our example below.
Another differnce from libraries to contracts is that LIBRARIES CAN NOT STORE DATA/TOKENS NOR ETHEREUM, so be careful
Below is the library I built just to demonstrate how can we add 2 new functionalities to uint, very simple functionalities actually, plus increments the uint that called it by 1 and plusplus increments by 2
pragma solidity ^0.5.0;
//library to add more functionality to uints
library uintPlus {
function plus(uint _self) public pure returns (uint){//function that adds 1 to the uint
return _self+=1;
}
function plusplus(uint _self) public pure returns (uint){//function that adds 2
return _self += 2;
}
Importing a library to a contract
Let me, shortly, introduce how the Ethereum Virtual Machine file system works.
If you see the file structure on the Remix IDE, on the left side, you can see that all the files are inside the folder browser
But when you tell the EVM to look for a file it starts looking one directore above the directory where the file is at! So it is like if the EVM does a cd .. before importing the new file, so, to get the library "connected" to our contract in another file from the same directory, simply import considering we are one directory above.
pragma solidity ^0.5.0;
import "browser/library.sol"; //importing as if we are one directory above where the file is at
contract specialUint {
}
Giving "super powers" to our uint
Now that the contract know where to find the library, you can already make the uints "inherit" our uintPlus
contract specialUint {
using uintPlus for uint; //uint "inherits" uintPlus functionalities
}
Testing the new uint functionalities
Let us make functions to see if the new "super uint" is working
contract specialUint {
using uintPlus for uint;
//function to call the new method added to ints
function sumOne(uint number) public pure returns (uint){
return number.plus();
}
//function to call the new method added to ints
function sumTwo(uint number) public pure returns (uint){
return number.plusplus();
}
}
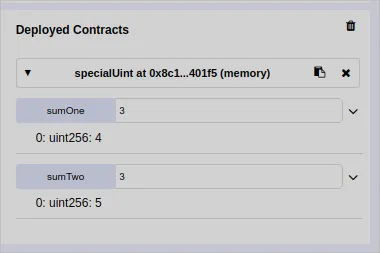
I have deployed the specialUint contract and here is it working
Leveraging libraries to automate events
You are very likely to use a lot of libraries while developing your Ethereum applications, and with time you will get very very bored of calling events, so we can leverage the functinality of libraries of adding functionalities to data types to make them automatically send events.
On this example we will alert the network of the operations that were executed with the following event on the uintPlus library
event added(address, uint, uint, string);
Address of the sender of the operation, uint of the original number, uint of the returned number and string describing which function was called
And changing the functions from the library to execute the events with the right arguments
Notice that I have removed the pure keyword
function plus(uint _self) public returns (uint){ //the function is not pure anymore
uint selfPlusOne = _self+1;
emit added(msg.sender, _self, selfPlusOne, "plus called");
return selfPlusOne;
}
function plusplus(uint _self) public returns (uint){//the function is not pure anymore
uint selfPlusTwo = _self+1;
emit added(msg.sender, _self, selfPlusTwo, "plusplus called");
return _self += 2;
}
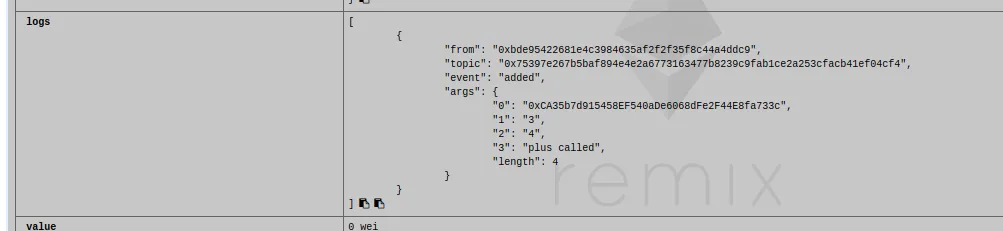
And if you check, we have succesfully raised an event from that
Libraries and security
If you follow the Ethereum tutorial series you most likely have noticed that I touch on the subject of security. It is because on contracts security is very important, as you can lose everything because of an overflow exploit or you can get your whole project hacked, and as contract are not mutable this can generate huge headaches (yes, I have taught how to make mutable contracts but that is not the norm haha)
This is why there are security libraries created
One os the most well known libraries is the "safe math" (there are variants so I grabbed a simple one)
https://github.com/aragon/zeppelin-solidity/blob/master/contracts/SafeMathLib.sol
NOTE:
I did a pull request to the SafeMathLib.sol above because they are using an older version of solidity and using the deprecated throw keyword
I have modified the code slightly to allow for a more intuitive usage, check it
pragma solidity ^0.5.0;
library SafeMathLib {
function times(uint _self, uint b) public pure returns (uint) {
uint a = _self;
uint c = a * b;
require(a == 0 || c / a == b);
return c;
}
function minus(uint _self, uint b) public pure returns (uint) {
uint a = _self;
require(b <= a);
return a - b;
}
function plus(uint _self, uint b) public pure returns (uint) {
uint a = _self;
uint c = a + b;
require(c>=a && c>=b);
return c;
}
}
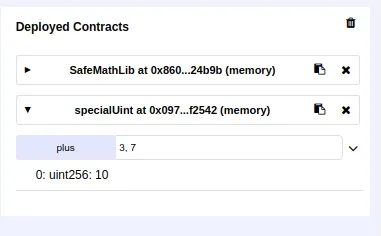
And I have also changed the a little bit our main contract to allow us to see how are we gonna call the plus from safe math
pragma solidity ^0.5.0;
import "browser/SafeMathLib.sol";
contract specialUint {
using SafeMathLib for uint;
function plus(uint number, uint secondNumber) public pure returns (uint){
return number.plus(secondNumber);
}
}
And of course the library works as expected
Curriculum
- (Part 5) Ethereum Solidity - Custom Access Modifiers, Security Breach Alerts, Assert And Require(PT 5)
- (Part 4) Ethereum Solidity Development - Inheritance,Working With Multiple Contracts And Simple Mutability(PT 4)
- (Part 3) Ethereum Solidity Development - Contract Mutability, DelegateCall And Calling Functions By Address(PT 3)
- (Part 2) Ethereum Solidity Development - Deploying, Securiy And ERC20 Compliance(PT 2)
- (Part 1) Ethereum Solidity Development - Getting Started + Lower Level Explanation (PT 1)
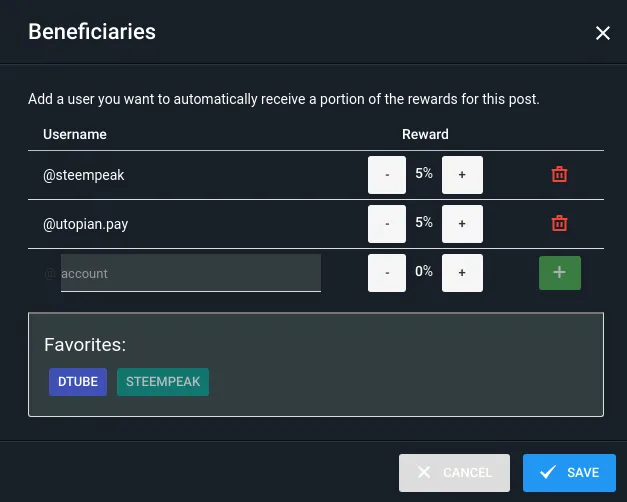
Beneficiaries
This post has as beneficiaries
@steempeak with 5%
@utopian.pay with 5%
using the SteemPeak beneficiary tool