
Repository
https://github.com/dart-lang/sdk
What Will I Learn?
- You will learn about the Basics of programming
- You will learn about Objects in Dart
- You will learn about Types in Dart
- You will learn about how Functions are Objects in Dart
- You will learn how to use closures and first class functions
- You will learn how to bind variables in Dart
Requirements
System Requirements:
- IDEA intellij or Visual Studio Code with the Dart Plugins
- The Dart SDK
OS Support for Dart:
- Windows
- macOS
- Linux
Required Knowledge
- The Dart SDK
- A dart supported text editor
- A little time to sit and watch a video and some patience to learn the language
Resources for Dart:
- Dart Website: https://www.dartlang.org/
- Dart Official Documentation: https://www.dartlang.org/guides/language/language-tour
- Dart GitHub repository: https://github.com/dart-lang/sdk
- Awesome Dart GitHub Repository: https://github.com/yissachar/awesome-dart
- Pub website: https://pub.dartlang.org
Sources:
Dart Logo (Google): https://www.dartlang.org/
Difficulty
- Beginner
Description
With Dart's roots in JavaScript, Java, C#, Smalltalk and Erlang; there are very few resources that teach Dart to non-programmers. As a result, it is difficult to get into Dart and subsequently the Flutter Framework, without knowing another programming language first. This runs counter to the notion that Flutter and Dart are easy to learn and be productive in. These video tutorials aim to rectify this shortage of information and provide a deep dive look into the Dart programming language.
Types in the Dart Programming Language
Dart is general purpose programming language that was originally designed by Google for client side development. The language is both Imperative and Object Oriented with some small functional features scattered throughout. With an Imperative language, a developer defines sequential instructions that build a program. This is further abstracted upon with the Object system in Dart. Every Type that can be assigned to a variable is an Object in Dart.

Dart contains seven main primitive types in its static type system: numbers, strings, booleans, lists, maps, runes and symbols. Numbers include Floats and Integers. Strings are used to represent text by using single and double quotations. Booleans are binary values that can either be True or False. Lists are zero indexable collections of data. Maps are collections with associative key-value pairs. Runes are UTF-32 code points which are used to create strings and characters. Symbols are symbolic names used for mirrors, invocations, and functions.
First Class Functions and Closures
A side effect of most types being Objects is that functions are also Objects in Dart. Functions are first class citizens in Dart because they also support all operations that are available to Objects. They can be assigned to a variable, passed as an argument to another function, returned from a function, stored in other Data collections, and created in any scope. Functions can have static type signatures and they can have dynamic type signatures. Functions can also be anonymous or in other terms, closures.
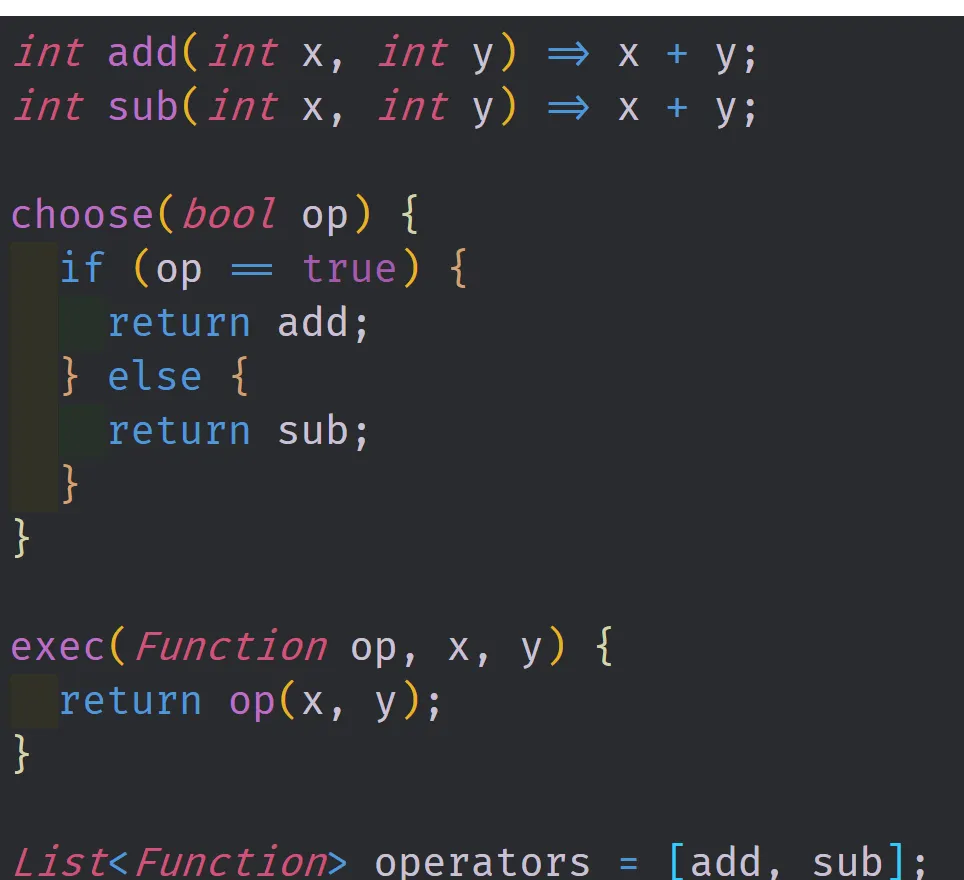
In the above image, there are examples of the traits mentioned above. Two functions add and sub are defined using single line notation. The choose function returns either add or sub depending on the boolean argument that is passed into it. The exec function takes in a function as an argument and that function can be any function that takes in two arguments. The operator list contains both the add and sub functions inside of it.
The Source Code for this video may be found here: https://github.com/tensor-programming/dart_for_beginners