In this video tutorial series, I will be sharing building a blockchain from scratch with just SHA256 hashing algorithm. After that, I am building a REST API on top of it with Express.js and make the blockchain decentralize.
The language I will be using is TypeScript, a superset language on top of JavaScript. Typescript offers static type checking, prevent runtime error and offer better class definition. With TypeScript, the variable can have types, which helps in debugging this app.
What Will I Learn?
Write here briefly the details of what the user is going to learn in a bullet list.
- Brief explanation on BlockChain
- Setup Block Class, Transaction Class and Blockchain Class in TypeScript
Requirements
Write here a bullet list of the requirements for the user in order to follow this video tutorial.
- Basic understanding of BlockChain
- Understanding of Typescript
- Understanding basic of Object Oriented Programming and Data Structure
Difficulty
Advanced
Description
What is BlockChain? (My original post explanation)
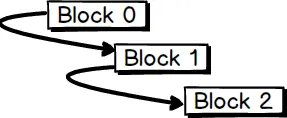
Blockchain is pass by 1 block to another block, and it is being chained.
let say Block n is the first block.
Block 0- is the first block (index = 0) , also known as genesis block. It contains transactions.Block 1- is the second block (index = 1), it contains transactions, part of signature andBlock 0Block 2- is the third block (index = 2), it contains transactions, part of signature andBlock 1
Initialize the project
Since, this is a typescript project, typescript need to be install. Simply just run npm add --dev typescript or yarn add --dev typescript.
Initialise Typescript project with the command tsc --init.
Transaction Class (src/transaction.ts)
In this class, I made a very simple transaction. This transaction basically allowed a person to send to another person a certain amount.
interface TransactionData {
from: string;
to: string;
amount: number;
}
from- Transaction from a personto- Transaction to another personamount- The amount of Transaction
Initialise Transaction Class
export default class Transaction implements TransactionData {
constructor(
public from: string,
public to: string,
public amount: number
) {
}
}
Making from, to and amount public allow us to access the transaction class's data easily.
Block Class (src/block.ts)
In the block class, there are 6 data.
interface BlockData {
index: number;
hash: string;
previousHash: string;
nonce: number;
transactions: TransactionData[];
key: string;
}
indexstating the number of blockhashsaved the hashed valuepreviousHashstored the previous hash valuenonceis a way for the blockchain to keep track of mining (mainly used to solve the algorithm)transactionis used to stored TransactionData class, refer to above classkeymake transaction, index, previousHash, and nonce into a string
Create a genesis block

In genesis block, we expect the index to be 0 and no transactions.
Initialise Block Class
export default class Block implements BlockData {
constructor(
public index: number = 0,
public hash: string = '',
public previousHash: string = '',
public nonce: number = 0,
public transactions: TransactionData[] = []
) {}
get key(): string {
return JSON.stringify(this.transactions) + this.index + this.previousHash + this.nonce;
}
public addTransaction(transaction: TransactionData): void {
this.transactions = [...this.transactions, transaction];
}
}
In the constructor, the block is initialise with the following data:

Using Getter method, we can get the key value.
get key(): string {
return JSON.stringify(this.transactions) + this.index + this.previousHash + this.nonce;
}
Then, we add in another function which is called addTransaction which takes in a single transaction, and add it into existing transactions.
public addTransaction(transaction: TransactionData): void {
this.transactions = [...this.transactions, transaction];
}
Blockchain class (src/blockchain.ts)
Blockchain Class is where the main logic begins. Blockchain class, has a lot of Block classes. Therefore the interface look like this:
interface BlockChainData {
blocks: BlockData[];
}
Recalled that the blockchain got started with a genesis block, so the setup for the blockchain class for genesis block is done in constructor.
export default class Blockchain implements BlockChainData {
public blocks: BlockData[];
constructor(genesisBlock: BlockData) {
this.blocks = [];
this.addBlock(genesisBlock);
}
// insert code here
}
To add new block, we use addBlock() function which takes in a block, and then add it into the blocks of Blockchain class. If the block is the first block / genesis block, create a custom previousHash. The hash will be generated with SHA 256 hashing algorithm in the next tutorial.
public addBlock(block: BlockData): void {
// if genesis block
if (this.blocks.length === 0) {
block.previousHash = "0000000000";
block.hash = this.generateHash(block);
}
this.blocks = [...this.blocks, block];
}
public generateHash(block: BlockData) {
return '';
}
Test out everything that we had done.
Create a file call app.ts in the src directory which will import all the Block, Transaction and BlockChain class.
Right now, this app.ts did was to add the block into blockchain.
import Blockchain from './blockchain';
import Block from './block';
let b = new Block();
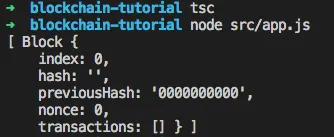
let bc = new Blockchain(b);
console.log(bc.blocks);
Then, run it with tsc and node src/app.js
Next Tutorial
In the next tutorial, I will add in sha256 hasing algorithm, setup the mining part, and making everything into functions before making these into REST API.
Source Code
The source code is available on github with respective branch name. For this tutorial, the branch is blockchain-1
Video Tutorial
Curriculum
This tutorial series will create a REST API with express.js on top of blockchain. The blockchain will be created from scratch with SHA256 hashing algorithm.
Posted on Utopian.io - Rewarding Open Source Contributors