Learn Python Series (#18) - PyMongo Part 1

What Will I Learn?
- You will learn what MongoDB is;
- what the differences are between a SQL versus a NoSQL database;
- how to install and run MongoDB on your own computer, how to view and interact with MongoDB via a MongoDB client manager (Robo 3T / RoboMongo in this case);
- how to install and import the PyMongo package, to use MongoDB together with your Python distribution;
- how to create and use a MongoDB database, collection, and documents;
- how to insert one and/or many documents to your collections of choice,
- how to retrieve / find one or multiple documents, given a certain (or empty) database query,
- how to count and return the number of documents found for a certain (or empty) query.
Requirements
- A working modern computer running macOS, Windows or Ubuntu
- An installed Python 3(.6) distribution, such as (for example) the Anaconda Distribution
- The ambition to learn Python programming
Difficulty
Intermediate
Curriculum (of the Learn Python Series):
- Learn Python Series - Intro
- Learn Python Series (#2) - Handling Strings Part 1
- Learn Python Series (#3) - Handling Strings Part 2
- Learn Python Series (#4) - Round-Up #1
- Learn Python Series (#5) - Handling Lists Part 1
- Learn Python Series (#6) - Handling Lists Part 2
- Learn Python Series (#7) - Handling Dictionaries
- Learn Python Series (#8) - Handling Tuples
- Learn Python Series (#9) - Using Import
- Learn Python Series (#10) - Matplotlib Part 1
- Learn Python Series (#11) - NumPy Part 1
- Learn Python Series (#12) - Handling Files
- Learn Python Series (#13) - Mini Project - Developing a Web Crawler Part 1
- Learn Python Series (#14) - Mini Project - Developing a Web Crawler Part 2
- Learn Python Series (#15) - Handling JSON
- Learn Python Series (#16) - Mini Project - Developing a Web Crawler Part 3
- Learn Python Series (#17) - Roundup #2 - Combining and analyzing any-to-any multi-currency historical data
Learn Python Series (#18) - PyMongo Part 1
In the previous Learn Python Series episodes, we started to work with JSON files, using serialization/deserialization techniques back and forth between JSON and Python dictionaries. Storing JSON data to files is of course a very convenient way to exchange data between applications and different computers (on the internet) but we can - and we will - take it even a few steps further by working with MongoDB and its official Python driver PyMongo.
Let's dive right in!
What's MongoDB?
MongoDB is - in short - a database engine. If you've experimented with programming here and there, you must have heard of "SQL" (Structured Query Language) which is a language with which you can interact with relational databases, such as for example MySQL. MongoDB functions differently, and its data is structured differently, than is the case with a relational database. MongoDB is a database engine which is oftentimes called of the form NoSQL, with which you store and retrieve data in a completely different way. And there are also several types of "NoSQL" databases, where MongoDB is of the form document datastore.
SQL versus NoSQL
Okay, so there are differences between SQL / relational databases and NoSQL databases, but which differences, why do those differences matter, and when to use what?
I could write an entire book about trying to (in-depth) answer the above questions, but to keep things short and clear, let's compare some features, strengths and weaknesses, between SQL and NoSQL databases:
SQL:
- your data is stored in tables with multiple fields and inside the tables are records;
- the data structure is very "strict" and if you want to add or change data properties, you need to change the database schema;
- data is structured in a relational matter, where you "connect bits and pieces" of data to eachother mostly via IDs of data stored in multiple tables, meaning data that doesn't belong to the exact same "data object type" is oftentimes stored "scattered accross" multiple tables, yet still relating to / joined to eachother via IDs;
- is used a lot in situations where each and every record in a table has the exact same data properties;
- it's good practise to store data "non-redundant" ergo "unique" and "once only".
NoSQL:
- works with "collections" (instead of tables) and "documents" (seen as "records"), at least for the document datastore type that MongoDB belongs to);
- data can be stored in a JSON-like way (name:value pairs) or as key:value pairs (depending on the type of NoSQL database, MongoDB is JSON-like (BSON actually: Binary JSON);
- the data model is non-relational, which means that data redundancy isn't considered a very important factor (causing the size of the database to grow substantially as compared to SQL solutions), but the upside is that data belonging to a certain "object" can be put all together in one place;
- the data structure is very flexible, so if you want to change something / add something to a certain "document" (record) you can do so with ease, without needing to change the database structure itself;
- it's very flexible yet also very fast to "quickly fetch all data belonging to a vertain data object".
PS: as time goes by and database development grows, the core differences between SQL and NoSQL database engines begin to fade away. PostgreSQL for example (an SQL / relational database by nature) nowadays also supports JSON like data storage and retrieval, although currently for that purpose lots of MongoDB specific advantages are still lacking in the PostgreSQL solutions.
Some MongoDB specifics
As said above, in MongoDB you store JSON-like data. "Under the hood" in MongoDB that data is stored in a binary format, BSON, binary JSON, but from a developer / user perspective just think of the MongoDB data as being JSON without the hassle of having to store and retrieve complete JSON structures to "flat" files. Because it's so flexible, the fun thing is that can very quickly develop applications on top of your MongoDB datasets, without needing to "architect" everything you want in your application beforehand (as would be the case with a SQL setup, requiring you to think about and know about all the ins & outs of your application and therefore data structure before beginning to develop it, otherwise you could get "into trouble" later on).
In MongoDB, you can store all the data in your model within a single "document". For example, in case you'd like to store everything about your own Steem account, you can do so within one single document! Not just your "account_name", "account_creation_date" , "account_about_info" (as you would in an SQL context), but you can add all your article posts, comments, your follows, your wallet, whatever you like within the same one "account" document! And even if you have loads of data stored regarding "account 1", you could have less, more or different data stored about "account 2". All that and you can still use matching (eg. ==) and comparison (<, >) type queries!
And to take things even further, MongoDB scales very well ("horizontally"), is RAM-efficient, you can "shard" data (handy for load balancing) and because the data is so self-contained (document 1 doesn't need to relate to / reference to document 2, therefore it's not "relationally oriented") load-balancing is relatively easy too.
Does it show I'm quite enthusiastic about MongoDB? ;-)
Using MongoDB with Python via "PyMongo"
Alright, so much for theory and conceptual MongoDB explanations; let's now try to actually use MongoDB together with Python! The PyMongo distribution is the "official way" to use MongoDB together with Python and it contains serveral tools for interacting with a MongoDB instance via Python.
Installing and running MongoDB itself on your system
In order to use MongoDB together with Python, you must of course first install and run MongoDB on your computer system. Since this is the Learn Python Series, the core focus of it is Python, so I suggest you visit https://docs.mongodb.com/manual/administration/install-community/ for installation instructions for either macOS, Linux and Windows regarding the installation of MongoDB Community Edition.
Managing and visually interfacing with MongoDB via "Robo 3T" (formerly "RoboMongo")
A convenient way to manage your MongoDB databases is by installing and running a MongoDB management console client on your computer system. "Robo 3T" (formerly named "RoboMongo") to be found and downloaded on https://robomongo.org/download is my personal favorite to do just that. It's available for macOS, Linux and Windows as well, allows for connecting to multiple MongoDB databases, has multiple views (you can inspect your MongoDB data in various ways), and it has an interactive MongoDB shell, including auto-completion tools, which is pretty convenient to quickly test some queries. (PS: For php / MySQL backgrounded people: Robo 3T / Robomongo does for you (and more) what you're used to with "phpMyAdmin".)
Installation of PyMongo to your (virtual) Python environment
The easiest way to install and use PyMongo is via:
python -m pip install pymongo
If all goes well, you're now good to go and start using MongoDB together with Python!
Establishing a connection to MongoDB
In order to connect Python to MongoDB, you first need to import the pymongo package, use the MongoClient class from it and set up the connection. Like so:
import pymongo
client = pymongo.MongoClient('mongodb://localhost:27017')
This means you want to connect to the default host MongoDB is running on (being localhost, on your computer system) and you'll be using the default port 27017. The above line could have also be written as:
client = pymongo.MongoClient('localhost', 27017)
or even as
client = pymongo.MongoClient()
... which will all, in most situations, do the exact same thing, and mostly depends on how explicit you want to be in defining how to establish your connection.
Interacting with a MongoDB database
What I've called "MongoDB" is actually a "MongoDB server" (which could run on your personal computer, it's then still called a MongoDB server!), and a MongoDB server can run multiple MongDB databases. In your Python code, you must specify which database you want to interact with.
To begin with, you don't have any running and the fun thing with PyMongo that in case the connection with the MongoDB server is established and it cannot find the database you want to interact with, it creates it on the fly. Let's instantiate a new database object db and connect to its (currently non-existent) database called test_mongo like so:
db = client.test_mongo
Inserting a document to a (new) collection with insert_one()
Ok, let's pretend, for now, to begin with, we are going to create a Utopian / Steem / Steemit like database, and in it could be multiple collections of documents, but let's start with the first collection called accounts and in it we're going to store one document (containing account data) in the following (JSON-like) format:
{
"account": "scipio",
"slogan": "Does it matter who's right, or who's left?"
}
We must now first specify the collection (accounts) we want to store this document in, within the selected database (test_mongo), and then we can insert this one document inside the accounts collection using the insret_one() method. Like this:
coll = db.accounts
account_data = {
"account": "scipio",
"slogan": "Does it matter who's right, or who's left?"
}
result = coll.insert_one(account_data)
If we then refresh and look into our Robo 3T MongoDB management interface, we get the following result:
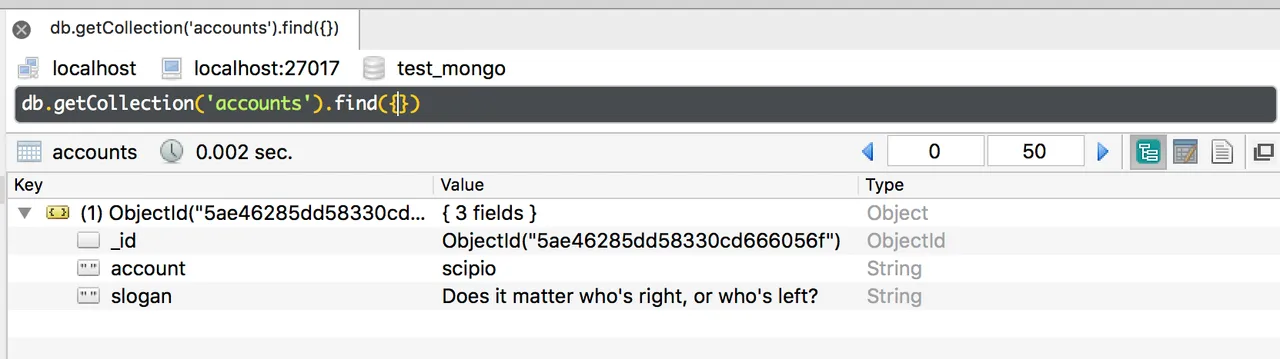
Cool! We did it! :-)
As you can see, the inserted document automatically received an ObjectId value associated to the _id key (we didn't need to manually insert just now), and we can return (or print) its value like so:
print('The ObjectId: {}'.format(result.inserted_id))
The objectID: 5ae46285dd58330cd666056f
Inserting multiple documents at once using insert_many()
If you need to insert more than one document to a collection, you could use insert_one() multiple times, or use insert_many() once, which is faster. To do so, just create a list of documents (in this case accounts holding some data) and insert that list as an argument to insert_many(), for example:
acc_1 = { "account": "stoodkev"}
acc_2 = { "account": "fabiyamada", "account_id": 261379}
acc_3 = {
"account": "jedigeiss",
"slogan": "IT Nerd, Risk Specialist, Musician, Cryptocoin Enthusiast, Banker, Gamer"
}
acc_list = [acc_1, acc_2, acc_3]
result = coll.insert_many(acc_list)
print('ObjectIds: {}'.format(result.inserted_ids))
ObjectIds: [ObjectId('5ae46693dd58330cd6660570'), ObjectId('5ae46693dd58330cd6660571'), ObjectId('5ae46693dd58330cd6660572')]
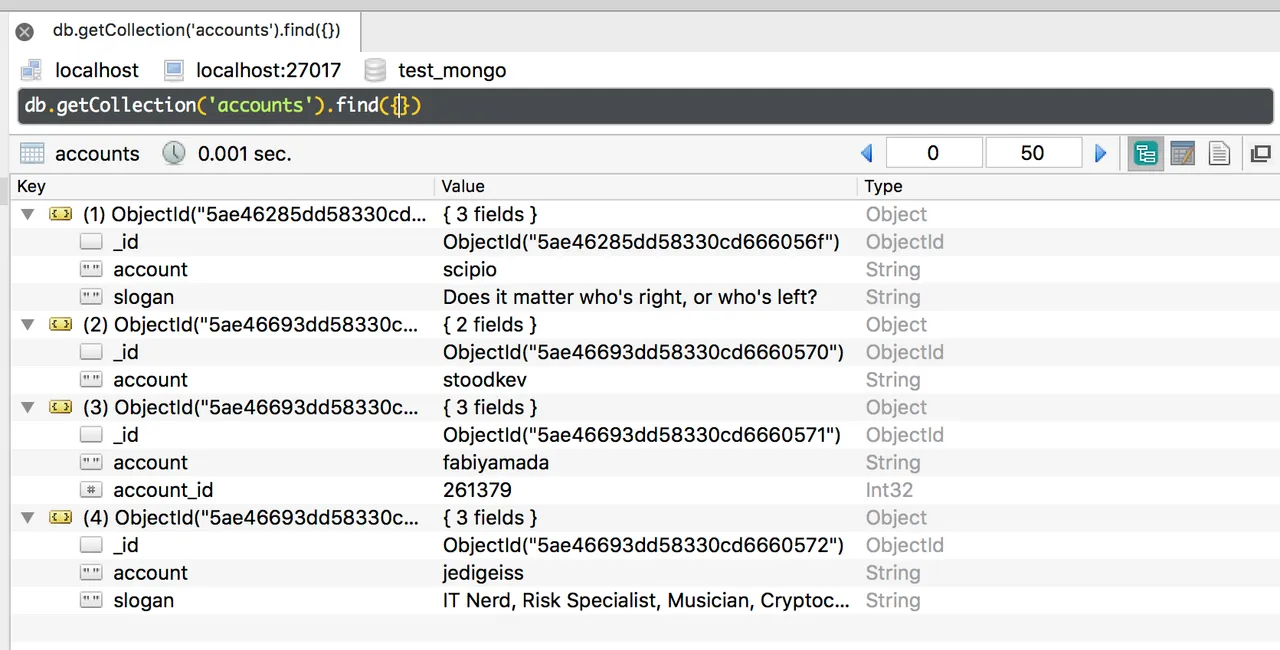
Nota bene 1: Because we've now inserted multiple documents at once, I called the attribute
result.inserted_ids instead of result.inserted_id!
Nota bene 2: I deliberately chose to insert multiple accounts, all containing an "account" (name) field, but account stoodkev I gave just that one field account where fabiyamada was the only account having an accout_id field and value. MongoDB is that flexible; you just add data to a document whenever you like, we can update the other account documents to have the same fields & values later if we like, or leave them as they are.
Retrieve one document with find_one()
Now that we have saved some data in the accouts collection within our test_mongo database, let's see how to find and retrieve one document given a (simple) database query. We're going to use the find_one() method to do that:
scipio = coll.find_one({"account": "scipio"})
print(scipio)
{'_id': ObjectId('5ae46285dd58330cd666056f'), 'account': 'scipio', 'slogan': "Does it matter who's right, or who's left?"}
Alright, that's exactly what we were expecting: as you can see, as an argument to the find_one() method, I passed in a key:value pair {"account": "scipio"} / dictionary, and as a result exactly one document - being the first one, and in case case only one, - is found and returned from the collection.
However, in case I would not pass any argument to the find_one() method, since scipio is the first (account) document we inserted, the same one document will be returned:
some_account = coll.find_one()
print(some_account)
{'_id': ObjectId('5ae46285dd58330cd666056f'), 'account': 'scipio', 'slogan': "Does it matter who's right, or who's left?"}
Retrieve multiple documents with find()
In case we're interested to find and retrieve multiple documents that match the given query we can use the find() method. Please note that the returned value (in case it matches at least one document) isn't (as you might have expected?) list of documents (dictionaries) but a so-called iterable Cursor object, which (at first sight) looks a little weird to work with, but has many helper methods that come in very handy (if you'll of course continue to follow along with my forthcoming Learn Python Series episodes!).
Let's just see how this works by using find() without passing in key:value pairs, meaning our intention is to retrieve the entire current accounts collection as the returned data:
all_accounts = coll.find()
print(type(all_accounts), all_accounts)
<class 'pymongo.cursor.Cursor'> <pymongo.cursor.Cursor object at 0x10bb37f60>
for each_account in all_accounts:
print(each_account)
{'_id': ObjectId('5ae46285dd58330cd666056f'), 'account': 'scipio', 'slogan': "Does it matter who's right, or who's left?"}
{'_id': ObjectId('5ae46693dd58330cd6660570'), 'account': 'stoodkev'}
{'_id': ObjectId('5ae46693dd58330cd6660571'), 'account': 'fabiyamada', 'account_id': 261379}
{'_id': ObjectId('5ae46693dd58330cd6660572'), 'account': 'jedigeiss', 'slogan': 'IT Nerd, Risk Specialist, Musician, Cryptocoin Enthusiast, Banker, Gamer'}
Counting documents matching a certain find() query using count()
Just as the Python len() function (to be used for example to count the amount of elements in a list), PyMongo provides us with a method count() to return the number of matching documents for a given query.
In case we want to return (or in this case: print) all accounts (documents) stores in the accounts collection, we just first run the find() method (without a key:value pair query as an argument) on our accounts collection and then append the count() method to it in order to the return the number of documents found. Like so:
num_accounts = coll.find().count()
print(num_accounts)
4
What did we learn, hopefully?
In this episode, I talked about MongoDB, being a type of NoSQL database environment, specifically a "document datastore", as opposed to SQL / relational databases. We discussed the differences between SQL vs NoSQL, and I hopefully got you to be just as enthusiastic as I am myself about using MongoDB together with Python.
We then briefly talked about how to install and run MongoDB, PyMongo as its Python driver, and Robo 3T / RoboMongo to conveniently view (and / or interact with) your MongoDB databases.
We then discussed databases, collections and documents, how to insert one or more documents, how to retrieve / find one or more documents, and how to count the number of documents in a collection matching a certain query (even a blank one).
But there's much more we can do with MongoDB and PyMongo & Python! We barely scratched the surface of all possibilities, so let's expand on what we learned today in the next sub-parts regarding PyMongo! See you in the next episode!
Thank you for your time!
Posted on Utopian.io - Rewarding Open Source Contributors